Basic Information
Inflammatory myopathies of adults are usually considered relatively rare and they can sometimes be very hard to diagnose as there are other medical conditions which are characterized by similar symptoms. There are three main types of inflammatory myopathies of adults and they include polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Quite often these medical conditions are associated with some other connective tissue diseases and they are associated with a rather high morbidity. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are inflammatory conditions by clinical and histological definition and they are differentiated by response to therapeutic methods directed towards the inflammation. Inclusion body myositis is a bit different as it commonly occurs only in people who are over 50 years old and it may only respond to immunosuppressive agents.
Symptoms
Dermatomyositis and polymyositis both have relatively gradual onset which may take weeks or months in some cases. The main symptoms include symmetrical proximal weakness of the muscles. Dermatomyositis may additionally be associated with several other characteristic symptoms such as the V signs, the shawl signs, the Gottron’s sign and a heliotrope rash. Certain patients may experience rashes which are characteristic for dermatomyositis but the rash itself does not have to be accompanied by the common muscle disease. The inclusion body myositis is blamed for weakness and atrophy of the quadriceps, finger flexors and wrist flexors. This weakness is in most cases distal as opposed to proximal weakness which occurs in other types of myopathies. All types of myopathies may be systemic and affect multiple organs inside the body. The joints may be affected too. In such case the condition manifest as non deforming symmetrical arthritis. When the gastrointestinal tract is affected, the disease manifests as intestinal vasculitis while inflammation affecting the lungs develops in the form of interstitial lung disease, aspiration or fibrosing alveolitis. The heart can be affected as well in the form of myocarditis, congestive heart failure or arrhythmias. There are also cases of myopathies which can be induced by various different types of medications and drugs. These include zidovudine, statins, quinidine, procainamide, interleukin 2, interferon alpha, heroin, D penicillamine, different types of corticosteroids, colchicines, cocaine, gemfibrizol, nicotinic acid, clofibrate, cimetidine, anti malarial agents and alcohol.
Diagnosis
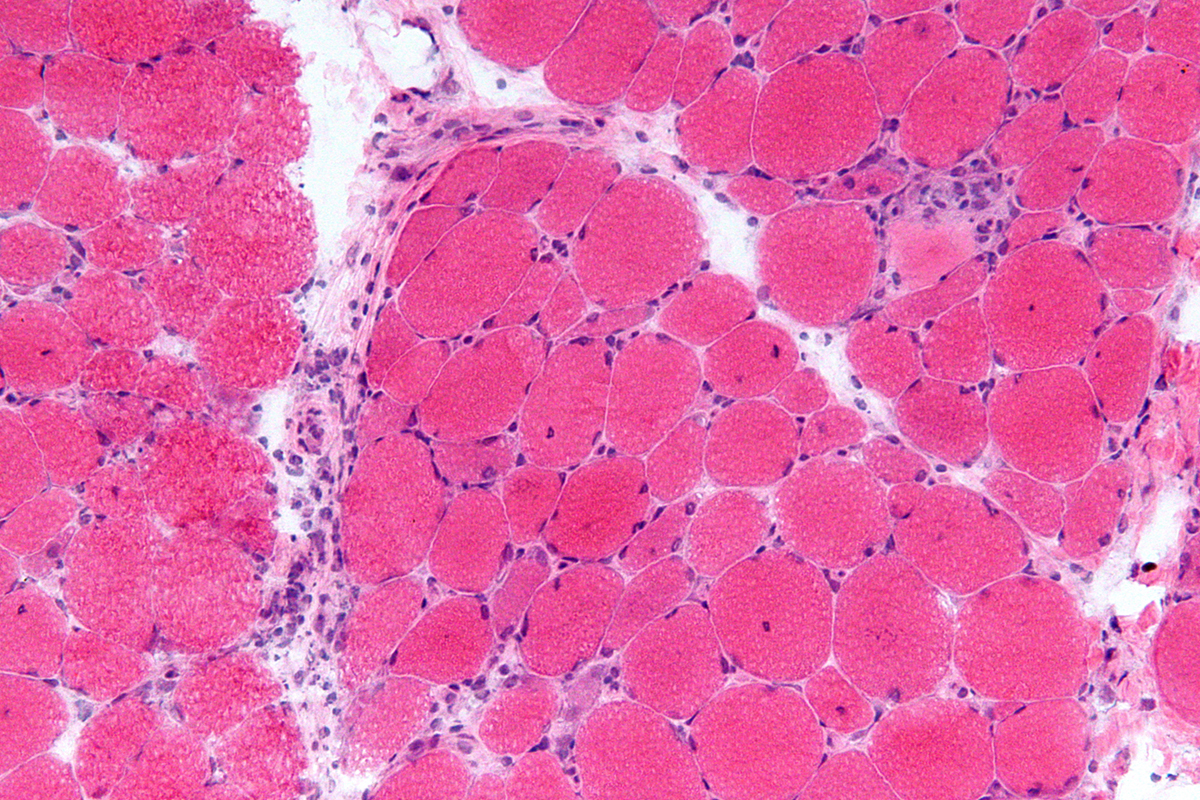
In order to be diagnosed fully and properly, inflammation of this type requires a muscle biopsy which is performed in all patients who may suffer from inflammatory myopathies. Proper diagnosis needs to confirm the disease and differentiate inflammatory myopathy from other types of medical conditions which may clinically resemble the condition. The doctor needs to be well informed about the patient’s entire medical history as well as family history. There are also certain laboratory tests which need to be performed so that the diagnosis can be accurate. Imaging and electromagnetic studies such as magnetic resonance imaging are also very helpful in determining the exact site for biopsy. Some patients with hypothyroidism may have very low levels of serum creatine kinase so they also require muscle enzyme measurements. Muscle biopsy needs to be carefully planned because in some cases the inflammatory condition may not be uniformly distributed within a single fascicle or a single muscle.
Treatment Options
Inflammatory myopathies are commonly associated with a relatively high rate of morbidity and mortality so that is why they need to be recognized and diagnosed as soon as possible and treated in a proper manner. The high mortality associated with inflammatory myopathies is usually a consequence of various different types of cancer and pulmonary complications. Out of all three different types of inflammatory myopathies dermatomyositis tends to be the easiest one to treat. In most cases, this type of inflammatory myopathy may respond well to intravenous immunosuppressants, intravenous immunoglobulin and steroids. Polymyositis may sometimes respond quite well to the type of therapy which involves intravenous immunosuppressants, but the actual response may vary from person to person. Inclusion body myositis is the hardest and most complex when it comes to treatment options and methods. The initial choice for most cases of inflammatory myopathies are still different types of corticosteroids. There are no controlled trials which might fully support the use of corticosteroids for the treatment of inflammatory myopathies but in most cases the dosage involves a gram of intravenous corticosteroids over the period of no more than 3 days. Eventual oral studies have not been studied enough yet. Corticosteroids are not effective enough in patients who suffer from inclusion body myositis. Some cases may also require the use steroid sparing agents which are very efficient in mitigating potential side effects of steroids. Apart from the mentioned there are also certain types of immunosuppressive agents which may be helpful in some cases of inflammatory myopathies and these include Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, intravenous gammaglobulin, mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate and azathioprine. Today scientist are investigating new and potentially successful treatments. Such experimental therapies might one day completely cure individuals suffering from inflammatory miopathies.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...