Scleroderma – Hardening of the Skin
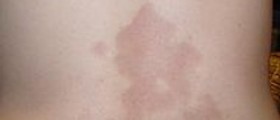
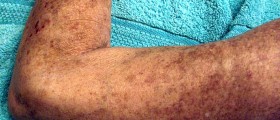
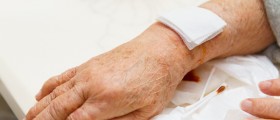
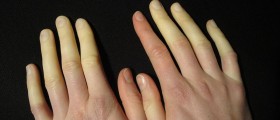
Scleroderma is a chronic type of medical condition which affectsthe skin and several other body organs as well. It is also sometimes referredto as systemic sclerosis. It is medicinally classified as an autoimmunerheumatic disease and it can be easily characterized by the tightening andthickening of the skin. It is considered as a fairly rare medical condition asit includes only 12 to 20 new cases per million people annually. Sclerodermamay affect persons from all different age groups, but those who are at thehighest risk are adult women. Scleroderma may also be associated with a buildupof scar tissue and damage to certain internal organs as well. The terminology mayget quite confusing as there are several different sorts of scleroderma anddiseases related to them, which all may lead to the development of certainmedical complications. These complications may be minor, but they may also bequite severe and even life threatening in some cases. Scleroderma may often beconfused with several other types of medical conditions such as nephrogenicsystemic fibrosis, eosinophilic fasciitis, scleromyxedema and scleredema. Thetwo main categories are localized scleroderma and systemic scleroderma.Localized scleroderma refers to the condition characterized by distinct skinlesions, while the other one suggests a condition which involves the skinsymptoms accompanied by internal organ disease. Localized scleroderma iscommonly characterized by skin lesions or morphea. In some minor cases, thismedical condition may be considered as only a cosmetic problem. Severe cases of localized scleroderma involvewidespread lesions, where the scarring and the thickness spreads to theunderying structures of the body which may include the fat, the muscles andsometimes even bones. When the localized scleroderma affects the face, thecondition is commonly referred to as en coup de sabre. Localized sclerodermamay be held responsible for reduced motion of the joints. Systemic sclerosiscan further be divided into two main categories which include the limitedcutanous systemic sclerosis and the diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. The accumulationof collagen and other proteins may extend to several internal organs such asthe vascular system, gastrointestinal tract, heart, lungs and kidneys. The limitedtype affects only the face, feet, legs, hands and the forearms, while thediffuse type may occur at virtually any area of the body. The earliest changeswhich may occur inside the body include certain types of immune system relatedproblems which may lead to the swelling, inflammatory conditions and tissuedamage. Damage to blood vessels may also occur and it may lead to other medicalcomplications such as gangrene or finger ulcers.
What Causes Scleroderma?
The exact causes of scleroderma are largely unknown butaccording to certain scientific studies, there are some genetic factors whichmay be held responsible for increased chances of getting the disease. Exposureto various different sorts of environmental agents and industrial solvents mayalso lead to the development of scleroderma.
How Is Scleroderma Diagnosed?
The main criteria for the proper diagnosis of sclerodermaare unusual swelling and thickening of the skin, especially when located on thehands. Additional criteria which may further contribute to the confirmation ofthe diagnosis include dilated blood vessels in the face, nail folds or hands, calciumdeposits in the skin, kidneys, muscles or the lungs. Most cases of sclerodermaare also accompanied by Raynaud’s phenomenon, difficulty swallowing andheartburn. Physical examination may sometimes need to be accompanied by furtherlaboratory tests and X-ray scans, depending on the individual case.
Treatment Options
There is no singular treatment method which can be used tocure those who suffer from scleroderma, but fortunately enough there are sometreatment options which may be utilized in order to alleviate the symptoms ofthe disease. One should also be well aware of the fact that the treatment planfor those who suffer from scleroderma usually involves a carefully guidedcooperation of a team of specialists. Those affected by the Raynaud’sphenomenon need to be keep their toes and fingers warm and protected from coldat all time. Kidney problems related to scleroderma need to be diagnosed asearly as possible in order to prevent some serious damage. Renal damage isprevented and treated by use of certain types of medicaments commonly used forblood pressure. These medications are referred to as angiotensin convertinginhibitors or ACE inhibitors. Those patients whose muscles are affected byscleroderma are commonly treated with certain types of immunosuppressivemedicaments, intravenous immunoglobulin and glucocorticoids. Interstitial lungdisease is commonly dealt with by utilizing cyclophosphamide. A similar lungrelated problem called pulmonary hypertension is usually treated with PDE-5inhibitors, endothelin receptor antagonists and prostacyclin like drugs. Thereare always new researches and scientific studies whose main goal is to find newand better treatment options for all those who suffer from scleroderma.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...