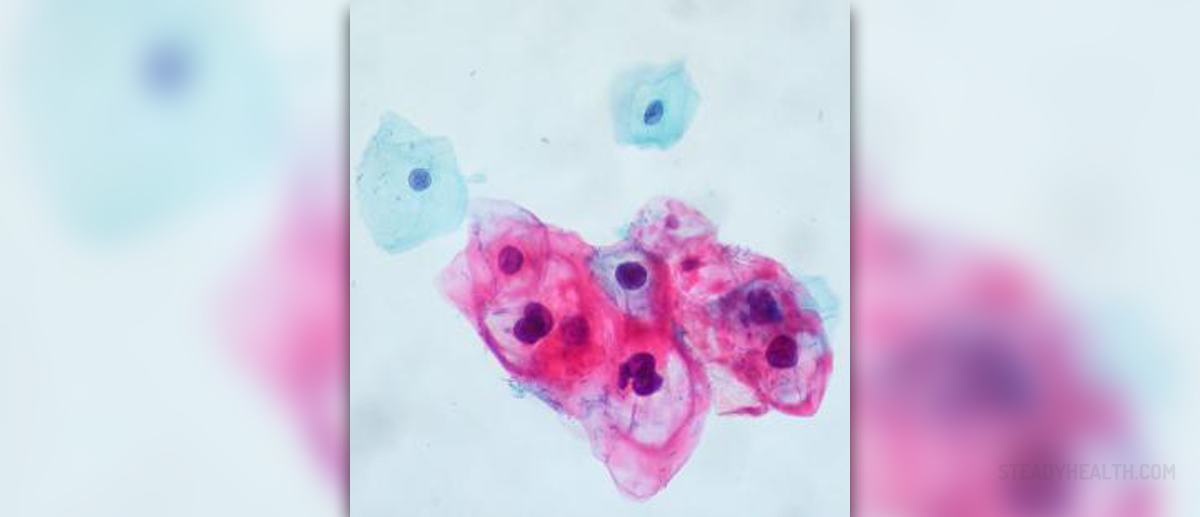
HPV (human papillomavirus) is a sexually transmitted virus responsible for many different types of cancers. In women the virus most commonly leads to cervical cancer. There are more than 30 types of human papillomavirus which affect both genders. They may cause changes to different parts of the body, such as, the lining of the mouth and throat, on the cervix and the anus.
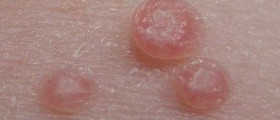
Human papillomavirus is a common virus. It is estimated that the virus may not cause any symptoms and simply go away on its own. However, in some cases the very presence of the virus (particularly in specific serotypes of the virus) leads to changes in the cells of the cervix or the lining of the mouth and throat. These changes have increased potential to develop into malignant tumors. On the other hand, certain types of the virus may be associated with benign skin changes such as warts and viruses.
HPV in Women
In the Unites States HPV types 16 and 18 are associated with approximately 70% of all cervical cancers. Furthermore, HPV types 6 and 11 are responsible for 90% cases of genital warts and they may in some cases be also connected with cancer of the mouth and throat.
The very presence of the virus is asymptomatic. It can be only detected with specific tests of the cervical cells collected during a Pap smear. If the smear test is normal and a woman is under 30, there is no need for an HPV test.
It is estimated that women, who have been exposed to the virus ,via sexual intercourse, who are smokers, as well as those who have had more than 6 unprotected sexual encounters, carry higher risk for cervical cancer.
Women should have regular gynecological exams. The gynecologist, can this way eveluate any suspicious changes on the cervix. Even if there are no noticeable changes, a Pap smear may point to the abnormalities in the cervical cells. This way cervical cancer can be identified in an early stage and treated successfully. Regular Pap smears can also identify precancerous lesions (the lesions which are an introduction to an actual cancer).
Prevention against HPV
Prevention of HPV transition is achieved by using appropriate protection during sexual intercourse. Condoms are most effective against the spread of HPV. Their efficacy is approximately 97%.
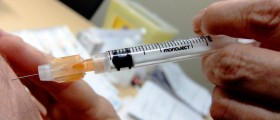
One more way of protection against harmful HPV in women is vaccination. The vaccine is administered to women between the ages of 9 and 26. Doctors recommend vaccination prior a girl becoming sexually active, for additional protection against HPV.


_f_280x120.jpg)






-Disease-Cause-Oral-Cancer_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...