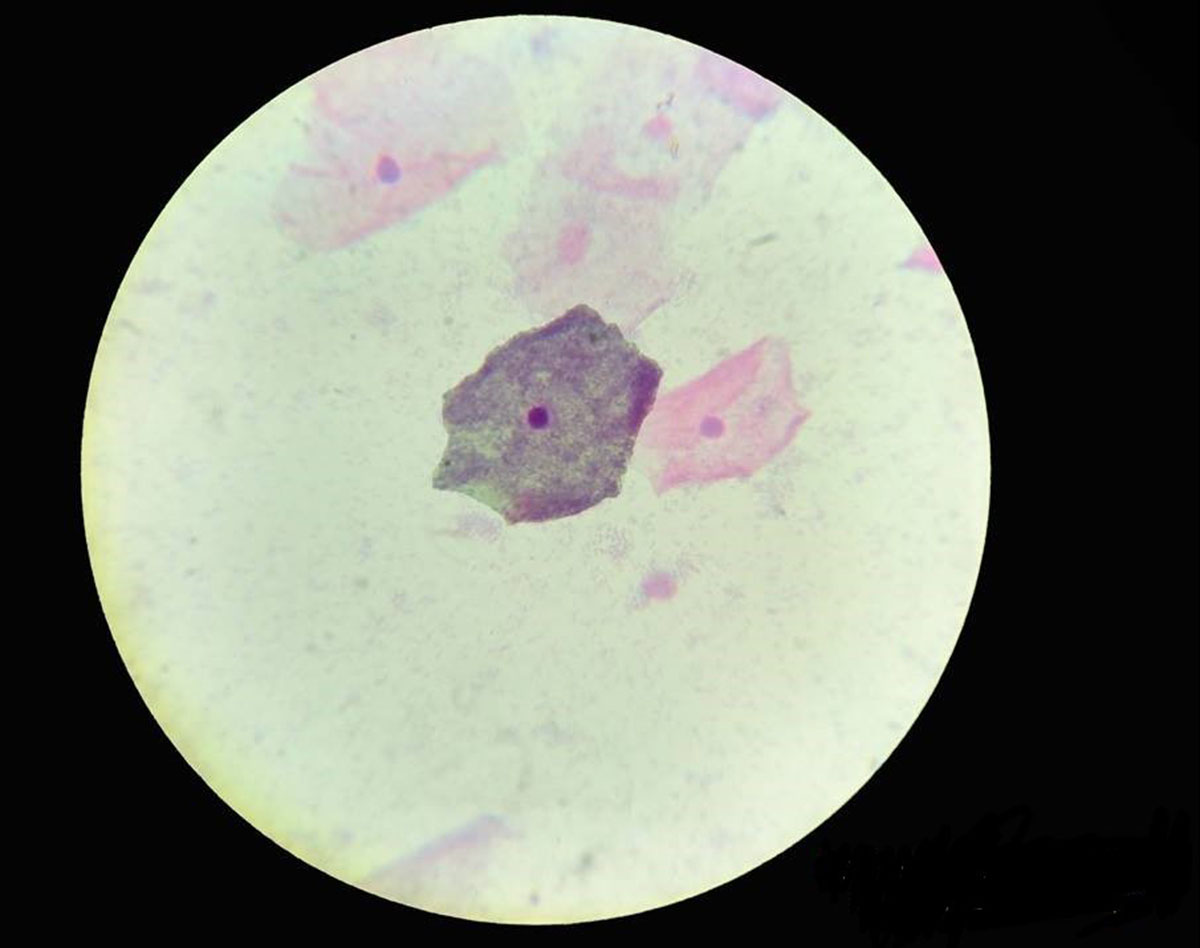
What is Pap Smear?Pap smear or the Papanicolaou test is a screening method that helps to detect cancer of the cervix in early stage. Abnormal pap smear result is not a replacement for pelvic examinations but an additional test for identifying cervical cancer.
A pap smear testing is conducted by analysis of the collected cells of the cervix under a microscope. This test aims to detect abnormal changes in the cervical cells. Every sexually active women and women over the age of 21 should undergo pap smear testing once every year.
Risk Factors for Abnormal Pap Smears
The biggest risk factor of having abnormal pap smear is human papilloma virus (HPV) infection. Women who have had many sexual partners and have not used protection are also at risk of abnormal pap smear. Family history of cervical cancer as well as smoking and usage of tobacco are other high-risk factors that cause abnormal pap smear.
Interpretation of Abnormal Pap Smears
Abnormal pap smear is “positive” pap test that indicates unusual changes in the cervical cells. Exact interpretation of the cause for abnormal pap smear test result is provided by a physician. The treatment is determined by the type of cells that are detected by the test.
Benign Cellular Changes These changes are caused by conditions that result in inflammation of the cervix. This includes: genital herpes, Chlamydia, yeast infections, gonorrhea and decline of estrogen in menopause.
Stages of Precancerous and Cancerous Cervical CellsASCUS or atypical squamous cells indicate cell abnormalities that are not caused by cancer. Cause of these changes is usually unknown.ASC-H are atypical squamous cells that may be caused by high-grade changes. This requires close monitoring due to a possibility of development of cervical cancer in the future. AGC or atypical glandular cells are benign changes in cells of endocervical or endometrial region.Cervical dysplasia is abnormal tissue but does not indicate cancer. It is classified according to the degree of cell abnormality:Mild dysplasia (CIN I) means that only few cells in surface of the cervix are affected. It is often caused by HPV infection.Moderate dysplasia (CIN II) is diagnosed when larger number of abnormal cells is present.Severe dysplasia (CIN III) indicates presence of abnormal cells in the entire surface of the cervix. This requires additional assessment with other procedures.Carcinoma in situ or AIS is diagnosed when cancerous cells have not yet spread below the surface of the cervix.Squamous intraepithelial lesion or SIL is a medical term for precancerous changes in cells of the cervix. Low-grade SIL indicates mild dysplasia while high-grade SIL signifies moderate to severe dysplasia or adenocarcinoma in situ.



_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...