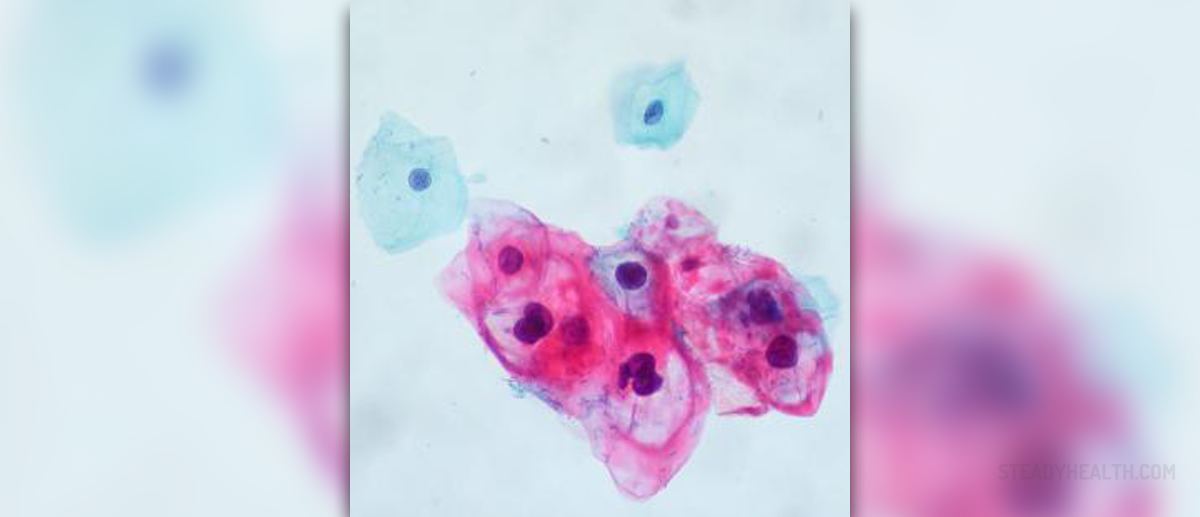
HPV or genital human papillomavirus is passed on through sexual contact affecting genitals but also mouth and throat. There are over 40 types of HPV sometimes without clearly visible symptoms. A person can have the HPV infection without knowing it and it happens that body manages to resist and clear the infection over the years. HPV infections can cause cancers in the genital area, most often cervical cancers. In great number of cases it manifests in genital warts and seldom warts in the throat.
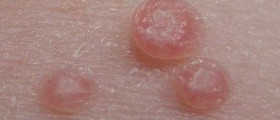
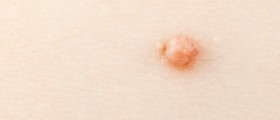
After sexual intercourse with the person carrying the HP virus weeks and months can passed before warts appear. The person withHPV sometimes does not have any symptoms and can transmit it to other people without knowing it. Warts are of different shapes, may appear single or in clusters, small or large. Gynecologists and other specialists can see warts during common medical examinations. After adequate treatment, warts can disappear. Otherwise, they may become larger, spread across other genital parts and they cause problems during sexual intercourse. Sometimes they disappear by themselves.
It does not necessarily mean that this will cause cervical cancer. Cervical cancer is diagnosed with a Pap test, screening and other medical tests. Every woman should do these tests for early diagnosis. If diagnosed at an early stage, signs and symptoms are not that serious and can be treated effectively. Symptoms of the cancer appear when the disease has already progressed. Therefore, it is advisable to visit a doctor regularly. Cancers inflict the penis, vagina, anus, and vulva as well.
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis or RRP inflicts the throat or other respiratory organs which results in the warts, heavy breathing and coarse voice. It rarely causes cancers and is quite rare.
HPV is typically transmitted through sexual contact, either vaginal, anal or oral. A person may not be aware of having HPV even years after the contact with infected partner. He or she can pass the virus to other sexual partners not knowing it. If infected with HPV, a pregnant woman can pass it on to her child who will be infected with RRP. People of all sexual orientations can get HPV, even more types of it. Among high risk groups are homosexuals and bisexual people.
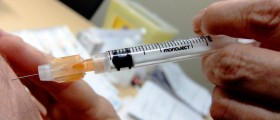
HPV changes the cells and inflicts inner or outer parts of genitals so sometimes warts can not be seen or months and years pass before becoming visible. HPV is quite common and 50 percent of people have it in some point of life. About 12,000 women a year in the USA have cervical cancers, about 1,000 of them have vaginal, about 4,000 men and women get anal cancers. To protect oneself, one can get three doses of vaccines against HPV preferably before the first sex. Cervarix and Gardasil are given to girls, aged 11 to 26, preventing cervical cancers or genital warts. Men get Gardasil vaccine. Condoms are also effective means of protection against HPV and many other sexually transmitted diseases. They are however, not 100 percent safe since HPV can affect other areas too. Since it is not possible to refrain from any sex, it is advisable not to change partners and try to have a faithful steady relationship with one person who has had very few partners earlier in life.
There is no treatment for the virus itself, but there is a therapy for all HPV related diseases. Warts and cancers are treated with prescribed medications.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...