Human papillomavirus, also known as the HPV is a virus responsible for several very severe health conditions. HPV is able to cause infection in the stratified epithelium of the skin or mucous membranes. It is estimated that approximately twenty four million Americans carry the virus in their bodies. There are about 200 known strains of HPV virus, but most of them are not harmful to humans. However, certain strains are associated with genital warts, and cancers of cervix, vulva, vagina, anus and penis.
Infection
Approximately 30 to 40 HPV strains are transmitted through sexual intercourse. Classic means of protection against sexually transmitted diseases, such as condoms, are not completely effective in the prevention of HPV. Human papillomavirus infects not only the penis or vagina, surfaces normally protected with the latex condom, but also the surrounding skin and tissues. Genital warts are always transmitted through sexual contact, and it is a quite common sexually transmitted disease. However, genital warts are temporary health complications and they are not associated with an increased risk of cancers. Actually, most of the HPV infections have low long-term significance, and they are gone in a year or two. However, persistent infections, that last more than two years, are high-risk infections and may cause the development of lesions on the cervix, so called cervical pre-cancer.
Symptoms of HPV infection and genital warts
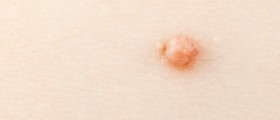
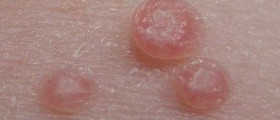
Genital warts are usually hard to spot until they develop on a form of bumps or abnormal skin growths in the genital area. Sometimes, genital warts are located inside of the vagina, on the cervix or inside of the anus, and extremely hard to spot. They may vary in shape and color – skin colored, or slightly red, flat or prominent. They may be painless or may cause burning sensation, ache and bleeding.
Unlike genital warts, other HPV infections associated with cancers are almost impossible to spot in the early stages. However, any kind of abnormality in the genital and anal region is to be considered as a warning sign.
Diagnosis
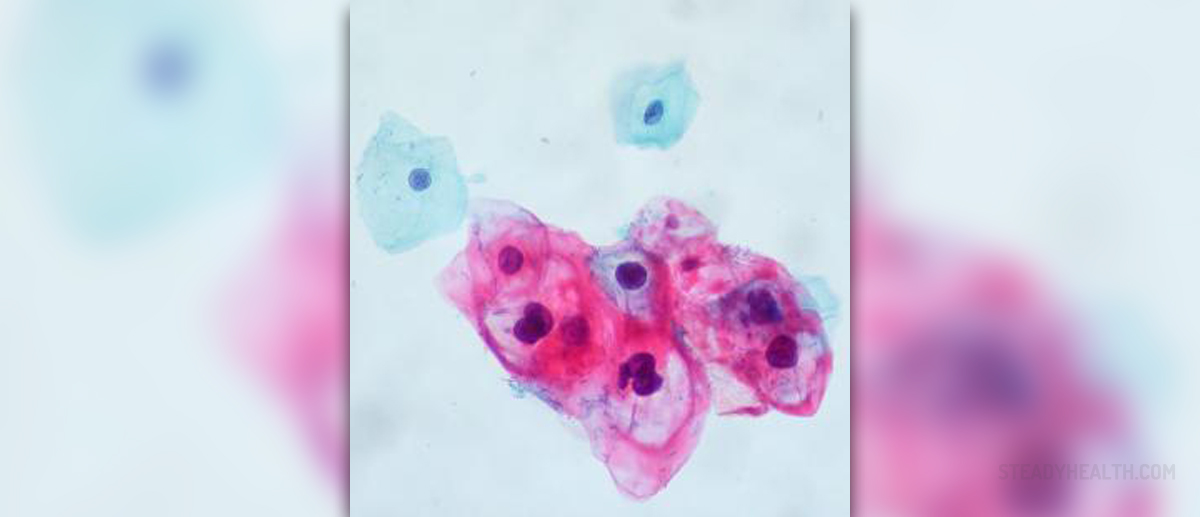
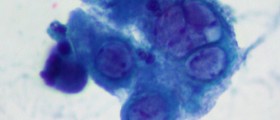
The presence of the genital warts or other HPV infections is diagnosed on the GYN examination. The Papanicolau test, also called Pap smear, is used to detect abnormal cervical changes and may indicate the presence of the cervical cancer or cysplasia. The early diagnosis of cervical cancer is crucial to proper treatment and positive prognosis. Regular Pap smears are the best way to prevent this terrible disease. Approximately 90% of all deaths caused by cervical cancers could be eliminated if they were detected earlier using this test.





_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...