Being proactive in healthcare is important for every woman. Problems related to the cervix, such as such as cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer may be drastically reduced by adhering to few simple advices and procedures, as described in the following article.
Procedures to follow against cervical cancer
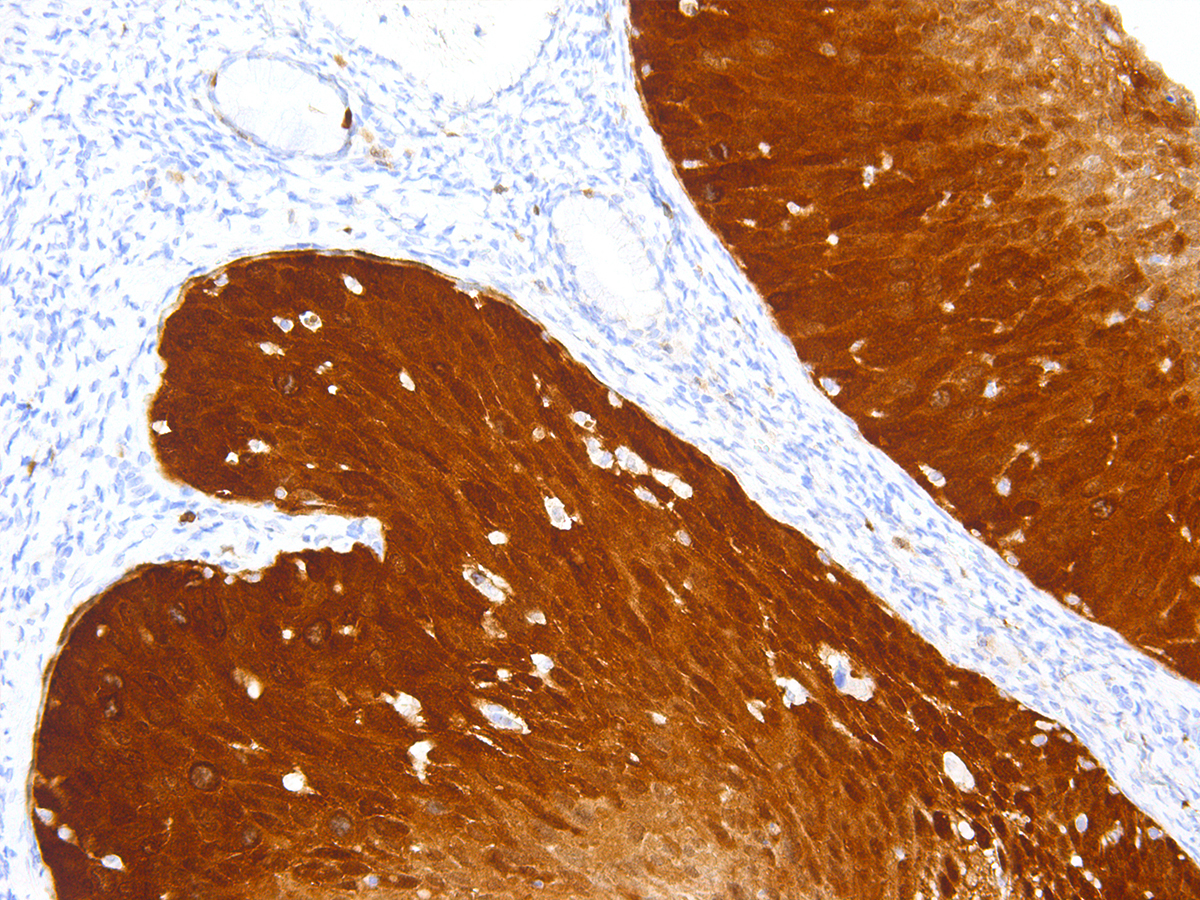
A Pap test (or Pap smear), which is important in cervical cancer prevention, should be performed regularly. It is conducted by smearing cells from female genital tract on a slide and microscopal examination of the cells. This test detects abnormal cervical changes, which indicate cervical cancer, or changes that may lead to cancer. As cervical cancer takes years to develop, this test is used to detect changes before they lead to cancer. It is a good idea to consult the physician in order to know when and how often to do the test.
Women infected with certain forms of human papilloma virus develop cervical dysplasia. Untreated cervical dysplasia may develop into cervical cancer. Vaccination with the HPV vaccine protects the receiver from these forms of human papilloma virus. There are two HPV vaccines on the market, (C)Gardasil (or Silgard) manufactured by Merx and Co. and (C)Cervarix, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline. Experts recommend regular examinations by Pap smear even after vaccination.
Advices to follow against cervical cancer
Following the physician's instructions is vital in prevention of cervical cancer. Many women never show up for follow-up treatments, colposcopy, and Pap tests for a variety of reasons. Typical reasons for this are lack of insurance, mistrust of doctor and misunderstanding of procedures. Physician's advice should be followed, and second opinion is always an option in case of disagreement. It is also vital to understand the follow-up plan completely.
Practicing safe sex is important both in prevention of unwanted pregnancy and in prevention of sexually transmitted diseases that may cause changes in cervix and ultimately lead to cervical cancer. Aforementioned human papilloma virus is spread by sexual skin-to-skin contact and penetration is not necessary for the virus to spread. Still, studies' results indicate that condoms, although not offering completely effective protection against the human papilloma virus, do offer a certain degree of protection.
Early symptoms of cervical cancer are rare, but any unusual symptoms should be timely reported to the physician. Symptoms that are commonly, although not necessarily related to cervical cancer, are, among others: pain during sexual intercourse, post-coital bleeding (bleeding from the vagina after the sexual intercourse), abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as abnormally heavy menstrual flow and bleeding between menstrual periods, as well as vaginal discharge.



_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...