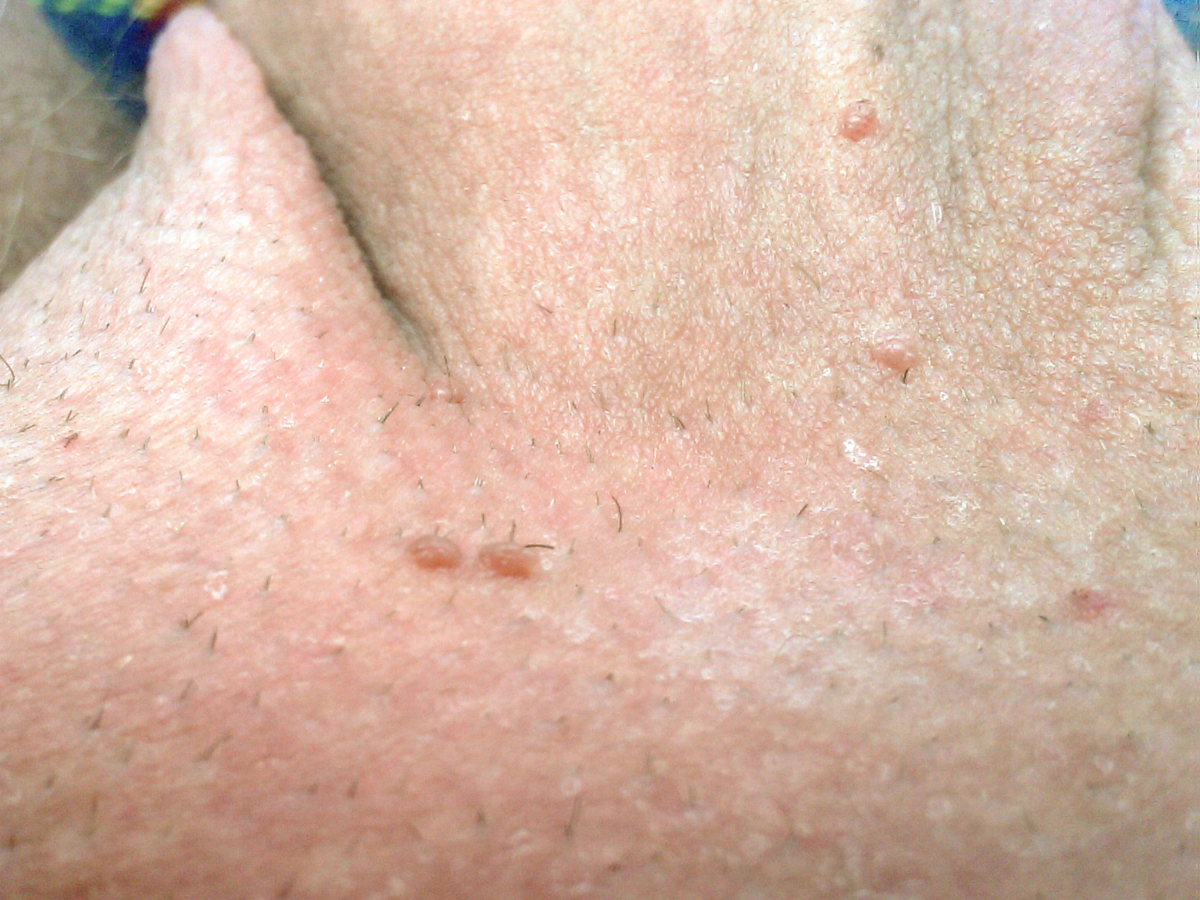
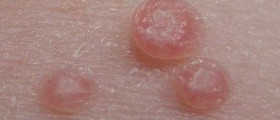
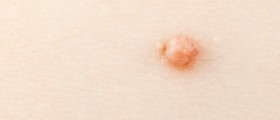
Genital warts, also known by the medical term condylomata acuminata, are among the most common sexually transmitted diseases. They look like the small, skin-colored bumps that are shaped like a cauliflower. They usually start small and gradually grow bigger in and greater number, forming large masses.
In women, they affect the vulva, vagina, cervix and uterus, as well as the area around the anus. In men they appear on the penis and scrotum and on the anus.
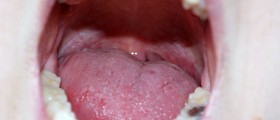
Both men and women can get these warts in mouth and throat as well, as a consequence of engaging in oral sex with a person who has the virus that causes them.
What causes genital warts
Genital warts are caused by a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV). So far there are around 100 different strains of HPV but not all of them cause warts and only 30 affect the genital area. Strains that affect the genitalia are called genital HPV and they affect around 50% of all sexually active men and women.
Human papillomavirus can be divided in two groups- high risk and low risk HPV. High risk HPV can cause cancer of cervix, vagina, penis, anus and throat. It is believed that the type 16 of HPV is responsible for half of all cervix cancer cases.
Low risk types cause genital warts and they do not cause cancer. It is believed that many people come in contact with these viruses but not all of them activate and it is sometimes hard to tell if a person has the virus or the warts or not. Warts begin as very small and until they are visible or palpable it is difficult to diagnose them. Because of this, the risk of transmitting or contracting genital warts is relatively high.
The most common way to get infected with HPV is through unprotected sexual intercourse. A person who has sexual contact with an infected partner has a 66 percent chance of contracting genital warts through vaginal, anal or oral sex.
Another way of transmission of HPV is through childbirth, if the mother has genital warts and baby contracts the virus passing through the birth canal. Babies who get infected usually develop warts in the throat and mouth.
It is believed, although there is no solid scientific proof yet, that HPV can be transmitted through shared objects, like towels and similar personal items or by medical instruments that are not properly sterilized.
Risk factors
The biggest factor of risk for HPV is unprotected sex. People who become sexually active early in life or who have multiple partners are at higher risk of getting genital warts. The medical history of previous sexually transmitted diseases also increases the risk.
The use of oral contraceptives can increase the risk of genital warts because it often excludes other forms of protection, like condoms.
Other factors include stress, smoking and alcoholism, impaired or weakened immune system or a trauma like surgery or serious illness.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...