Diabetes mellitus, or simply diabetes, is a group of the metabolic diseases in which patient has high blood sugar levels. Low sugar levels may result from the body’s inability to produce insulin or because cells don’t respond properly to insulin. According to this, there are two major types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is characterized by body’s failure to produce insulin, in which the patients are required to inject insulin daily; and Type 2 diabetes, the other kind of diabetes disease, that is distinguished by insulin resistance.
Statistics
Both Type 1 and 2 are chronic conditions that typically cannot be cured. It is estimated that at least 171 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes. That makes astonishing 2.8% of the population. Type 2 diabetes is by far the most common, and it affects approximately 90 to 95% of the U.S. diabetes population. Type 2 diabetes is especially dangerous as it can go undetected for a decade or longer. Many of the Type 2 diabetes sufferers are actually otherwise healthy and slender individuals, and don’t necessarily fall into the category of the obese and inactive population. A proper diagnosis and early testing is essential because unmanaged diabetes often leads to heart diseases, stroke, kidney failure, leg amputation and blindness.
Risk factors
Type 2 diabetes is due primarily to lifestyle factors and genetics, it is most commonly linked to obesity and inactive lifestyle. Type 1 diabetes is also partly inherited and then triggered by certain infections or other autoimmune disorders. However, certain portions of population are at slightly higher risk of developing diabetes:People who are overweight and older than 45People with hypertensionPeople with low levels of “good” cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein)People with family history of the diseasePeople who are non-CaucasianTesting for diabetes
As Type 2 diabetes may go unnoticed for years, it would be the best to get tested every three years. Testing may also help to detect if the person is in so-called pre-diabetic phase. In pre-diabetes glucose levels are severely elevated, but they are not enough high to be considered for signs of Type 2 diabetes. Regular monitoring and serious life-style moderations may help these patients to avoid developing diabetes. Also, regular testing of blood sugar can help reduce one’s risk of having long-term complications from diabetes.
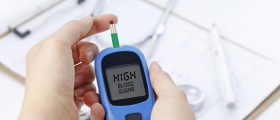
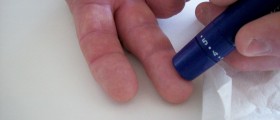
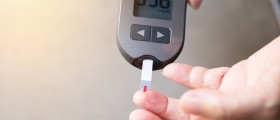
Blood sugar levels are measured in the doctor’s office using the traditional method of pricking the finger with a small, sharp, needle and putting a drop of blood on a test strip and then placing the strip into a meter that displays your blood sugar level. The procedure is painless and modern devices may provide accurate results in 15 seconds.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...