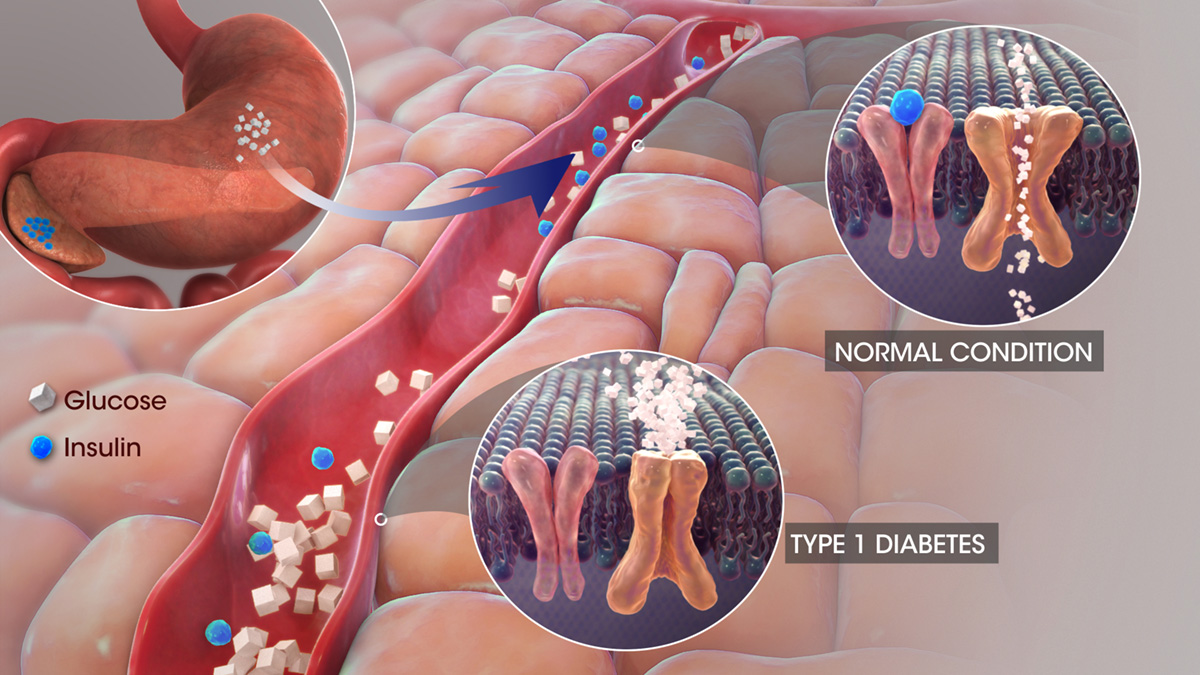
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that usually affects the children, adolescents and young adults. This condition is also known as juvenile diabetes and insulin-dependent diabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when body’s immune system attacks pancreas cells that produce insulin. Because their body no longer makes insulin, individuals affected by type 1 diabetes depend on insulin injections for life. Exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown but it is the most common form of diabetes that strikes children. It is believed that genetics plays a role in development of this disease as well as certain environmental triggers such as exposure to some virus. Type 1 diabetes entails the risk of blindness, kidney failure and even premature death.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in children are the same as those in adults. The symptoms in children usually develop suddenly, over a few weeks. Common symptom is increased thirst. Because of that, a child drinks more than usually which leads to frequent urination as another symptom of juvenile diabetes. Blurred vision and fatigue are also caused by this type of diabetes. The condition is accompanied with weight loss even though a child may have increased appetite. Affected child may have fruity odor in the breath and experience itching especially in the area of genitals due to yeast infection. Behavioral changes can be noticed too in children with type 1 diabetes. Labored breathing is also a symptom of this type of diabetes.
Dangerous complication of diabetes is a condition known as ketoacidosis that results from severe insulin deficiency. Without insulin, excess acidic ketones build up in the bloodstream and the blood becomes too acidic. Ketoacidosis is common in type 1 diabetes and can be life threatening if left untreated. Signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, muscle stiffness, rapid breathing and weight loss.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Type 1 DiabetesTo diagnose type 1 diabetes in a child, a doctor will order glycated hemoglobin (A1c) test that can show an average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. If A1c level is 6.5% or higher it indicates diabetes while the level between 6 and 6.5% indicates pre-diabetes or high risk of developing diabetes. There are other tests that can be used to diagnose diabetes, such as random blood sugar test and fasting blood sugar test. Blood and urine samples can be taken periodically to check levels of cholesterol and functions of the thyroid, liver and kidney. Type 1 diabetes is incurable but can be managed with insulin, healthy diet, regular exercise and monitoring of blood sugar levels. There are different types of insulin and it may be given through injections or pump.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...