Diabetes-Overview
Diabetes refers to a group of metabolic diseases. It mainly affects how the body uses blood glucose, commonly known as blood sugar. When a person has this disease, it means that there is too much glucose in their blood.
It is not that uncommon for a person to have diabetes. As of the year 2000 it has been estimated that at least 170 million people all over the world suffer from this disease.
The symptoms of diabetes include blurred vision, frequent urination, inexplicable weight loss, increased thirst accompanied by extreme hunger, tiredness and fatigue, sores that take very slow to heal, and recurrent infections. As soon as a person spots these symptoms, it is vital that they contact their physician immediately. Diabetes, if left untreated, may cause other complications, such as low or high blood sugar, increased ketones in one’s urine (a toxic acid that is the produce of the body’s starvation for energy, in which they begin to break down fat), kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, bone problems, skin and mouth conditions, eye damage, etc.
Causes of Diabetes
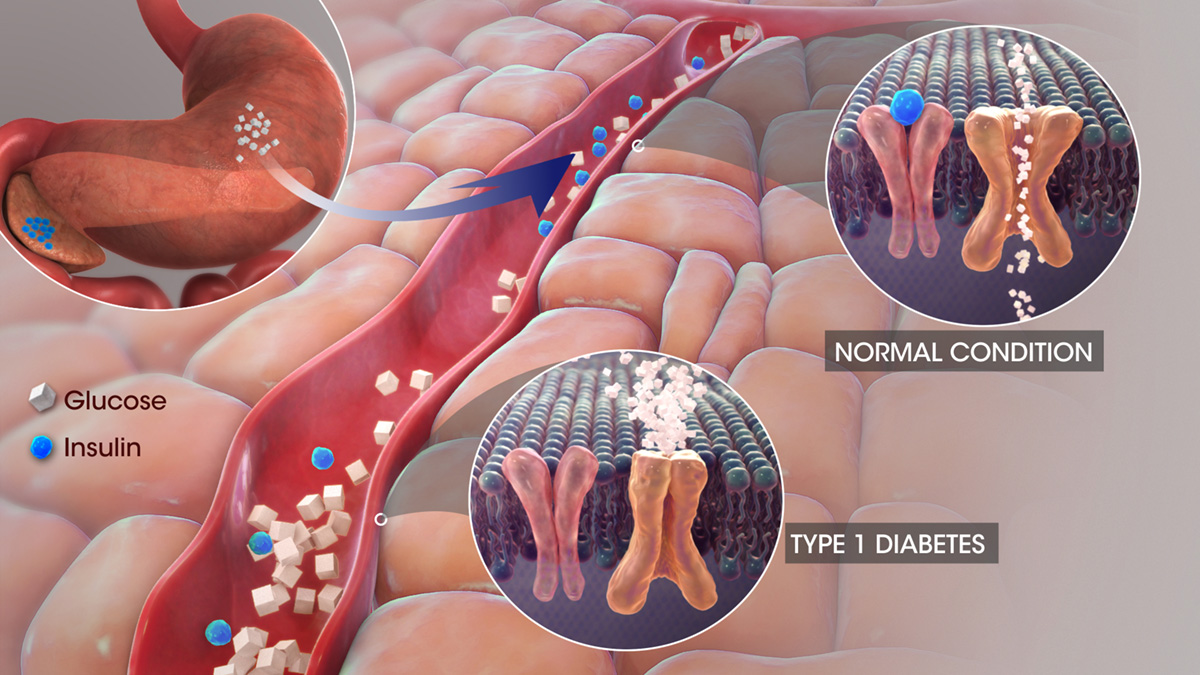
There are three types of diabetes, each disrupting the normal secretion of insulin in different ways. Insulin plays a very important role in the body’s energy production. During digestion, sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream. Normally, sugar then enters cells with the help of insulin. This hormone comes from the pancreas. When a person eats, the pancreas secretes insulin into their bloodstream. As insulin circulates, its properties are the ones that allow sugar to enter the body’s cells. Insulin lowers the amount of sugar in the bloodstream.
Types
Type 1
It is also called juvenile diabetes because the persons that get it are usually under 20. It is mainly believed that this is an autoimmune disorder. This means that the body’s immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that are in charge of the production of insulin. There might be a genetic predisposition for this type of diabetes, but it is highly unlikely. The other cause may be environmental factors, such as some viral infections. This type of diabetes lasts for life and insulin replacement therapy must continue throughout.
Type 2
In this type, the cells of the body become resistant to the action of insulin. This causes the sugar to build up in the bloodstream. The causes of this type seem to be inactivity and being overweight (especially having too much abdominal fat). Also, genes may have a lot to do with causing this particular type, but doctors think hat with a healthy lifestyle the risk decreases considerably.
Gestational Diabetes
This diabetes is acquired during pregnancy, when the placenta produces hormones that sustain the pregnancy, but that at the same time, make the cells more resistant to insulin. It usually













Your thoughts on this
Loading...