
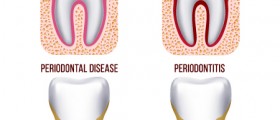
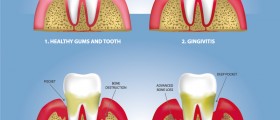
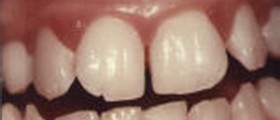
Gingivitis is the inflammation of gum tissue that usually occurs owing to the bad oral hygiene. Gingivitis usually outbreaks as a response to profuse formation of bacterial plaque. If not treated it may progress to perodontitis and eventually lead to serious damage to bone and even a tooth loss.
Symptoms
Symptoms of gingivitis correspond to classic signs of inflammation: swollen and painful gums, bleeding while brushing, bright red or purple colored gums, bad breath and bad taste in the mouth.
Some symptoms may indicate problems that are more serious and require immediate medical attention:Bad breath that lasts for more than 24 hoursTeeth look longer because of gums shrinking away from them.Mouth feels out of alignment when patient shuts because teeth come together in a different way.Partial dentures fit differently.Pseudopockets form between teeth and gumsTeeth are loose and may fall off.Causes
Local irritants usually cause gingivitis. Plaque-induced gingivitis is the most widespread type of gingival diseases. Bacterial plaque and food particles accumulate in the small gaps between the teeth and release toxic chemicals. Bacteria produce chemicals, such as degrative enzymes, and toxins, such as lipopolysaccharide causing the inflammation of gums as well as the swelling of gingiva resulting in pseudopocket formations.Other causes, besides bacterial plaque, are certain viral and fungal infections, hormonal misbalance, low nutrition diet, use of certain medications, etc.
Self-help techniques
A pinch of salt in a glass of lukewarm water will make a perfect gargle solution that can help swelling in the mouth. Clove oil should be used to rub gums and a regular use of anti bacterial mouthwash will reduce swelling of the gums. Cetylpridinium chloride and domiphen bromide are the active ingredients in mouthwash that reduces dental plaque.
Vitamin C rich diet will affect gum health significantly. Patients deficient in vitamin C are more prone to develop periodontal diseases. Diet should consist of plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables and fibers. Patients should avoid sugar, fruit juices, white flour and rice, soft drinks and syrups.
Regular visits to dentist are vital to prevent gingivitis from reoccurring. Dentist will clean patient’s teeth and gums, remove the plague and give some precious advices. Patients should use floss and brush after every meal.
To prevent periodontal diseases and suppress gingivitis, as the first sign of possible complications, patients should agree to some simple methods of treatment. It is crucial to understand that only patients themselves may save their own teeth from decay and falling off.
Proper flossing and brushing are of the greatest importance. Good oral hygiene will take just about 3 to 5 minutes twice or three times a day. Proper brushing should be at the gumline, because this is the plaque-forming area and this is where the gingivitis usually outbreaks. Brush should be positioned at 45-degree angle to teeth so that half of a brush cleans gums while the other half cleans teeth.
It might be good to have two toothbrushes so that one can dry out while patient is using another. A proxa brushes are specially designed to reach places under the crown or bridge. They are available in most of the drugstore and they look like small bottlebrushes.
Studies show that electric rotary toothbrush removes 98.2% of plaque while hand brush removes only 48.6% of it.
Gingivitis is often called “periodontal osteoporosis”. That is why patients should include a plenty of calcium in their diet to strengthen the bones and prevent shrinking and fragility of the jawbone.
Jaw massage will increase healthy blood flow into the gums while scraping the tongue removes bacteria and toxins.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...