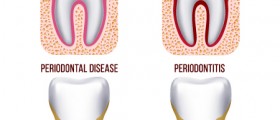
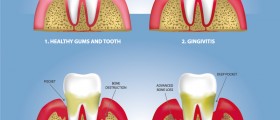
Gingivitis is a non-destructive periodontal disease characterized by inflammation of the gum tissue. This unpleasant condition leads to many, often painful, symptoms. Gingivitis is also associated with one very severe complication – periodontitis. When left untreated, gingivitis may progress to this serious stage of periodontal disease, which affects all of the tissues that surround and support the bone. In periodontitis, the alveolar bone around the teeth gradually decays and may lead to loosening and even a complete loss of teeth. Periodontitis is always preceded by gingivitis, and this is why it is so important to learn more about this common condition and to understand how to prevent it.
Signs and symptoms of gingivitis
Classical signs of inflammation that affects the tissues of the oral cavity typically characterize gingivitis. In gingivitis, the gums normally appear swollen and red or even purple. The gums are very tender and usually painful to touch. In most of the cases, the gums will bleed after even the gentlest brushing or flossing. Some of the patients will suffer from an unpleasant odor coming from the mouth.
Causes of gingivitis
Gingivitis is typically caused by accumulation of bacteria on the tooth surfaces. This bacterial plaque is something that normally accumulates on the daily basis. Regular and proper oral hygiene is aimed to remove this bacterial biofilm before it hardens, and prevent colonization by microorganisms, which may be pathogenic. Plaques usually accumulate in gaps between the teeth, in the gingival grooves and in claps of Removable partial dentures. Bacteria normally produce toxins and digestive enzymes, which trigger the inflammatory response. If plaques are not properly removed, it initiates body’s host response, as the tissue tries to protect itself from infection.
Prevention of gingivitis
Since gingivitis typically occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene, the first step to prevention is to improve the oral hygiene habits. This includes regular and proper brushing and flossing, at least two times a day. Proper brushing is essential to prevention, and it is done by placing the bristles along the gum line at the 45-degree angle. The tooth surfaces are gently brushed using a vibrating back and forth rolling motion. To brush behind the front teeth, one should tilt the brush vertically and make a couple of up and down strokes using just a half of the brush. The biting surface is brushed using a gentle back and forth scrubbing motion.
It is also important to replace the toothbrush every three to four months since the microbes can grow even on the toothbrush bristles and handles.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...