What Is Periodontal Gum Disease?
Periodontal Gum disease is an inflammation of the tissues that surround the jaw bones and support the teeth. It is generally a chronic condition that eventually leads to tooth loosening and falling out. Periodontal gum disease is generally caused by a buildup of plaque, an invisible sticky layer that contain bacteria. Toxins produced by bacteria are the leading cause of gum inflammation. The plaque forms on the teeth and if it is not taken care of in a timely manner it leads to formation of pockets between the teeth. Food particles easily collect inside these pockets and additionally contribute to gum inflammation.
Clinical Characteristics of Periodontal Gum Disease
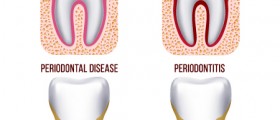
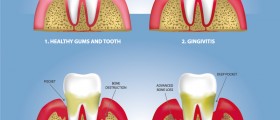
Periodontal gum disease may develop in several forms. Gingivitis is one of them and features with swelling and bleeding of the gums, bad breath and bad taste in the mouth. Gingivitis can be brought under control with teeth-brushing and flossing. In case a person develops acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis the affected gums are sore and covered with a whitish membrane. Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is treated with antibiotics. And finally, periodontitis occurs once the bacteria reach and destroy the connective tissues as well as bones. This is the most severe form of periodontal disease. The teeth are exposed and become very sensitive to temperature changes. Pockets between the teeth deepen and plaque in the surrounding area is very difficult to remove.
Treatment, Prevention and Reversing of Periodontal Disease
Even if the condition is diagnosed one may prevent its further progression and prevent many complications of the disease. Apart from special treatment and procedures performed by a dentist and a specialist in periodontal disease a patient can stick to certain routines that may decelerate the progression of periodontal disease.
In the first place it is essential to adopt a strenuous daily oral hygiene routine. This can be very effective in reversing periodontal gum disease. One is supposed to brush teeth thoroughly after getting up and before going to bed. Furthermore, teeth must be brushed after each meal and even after snacks.
The mouth should be rinsed with a good antibacterial mouthwash for at least 30 seconds twice a day. The process of rinsing can efficiently eliminate bacteria trapped in the gum pockets. Flossing is also a significant part of every day oral hygiene routine. And finally, one may benefit from powerful oral irrigators available on the market. They blast food particles out from the pockets and between the teeth, hence remove culprits responsible for inflammation.










-Disease-Cause-A-Stroke_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...