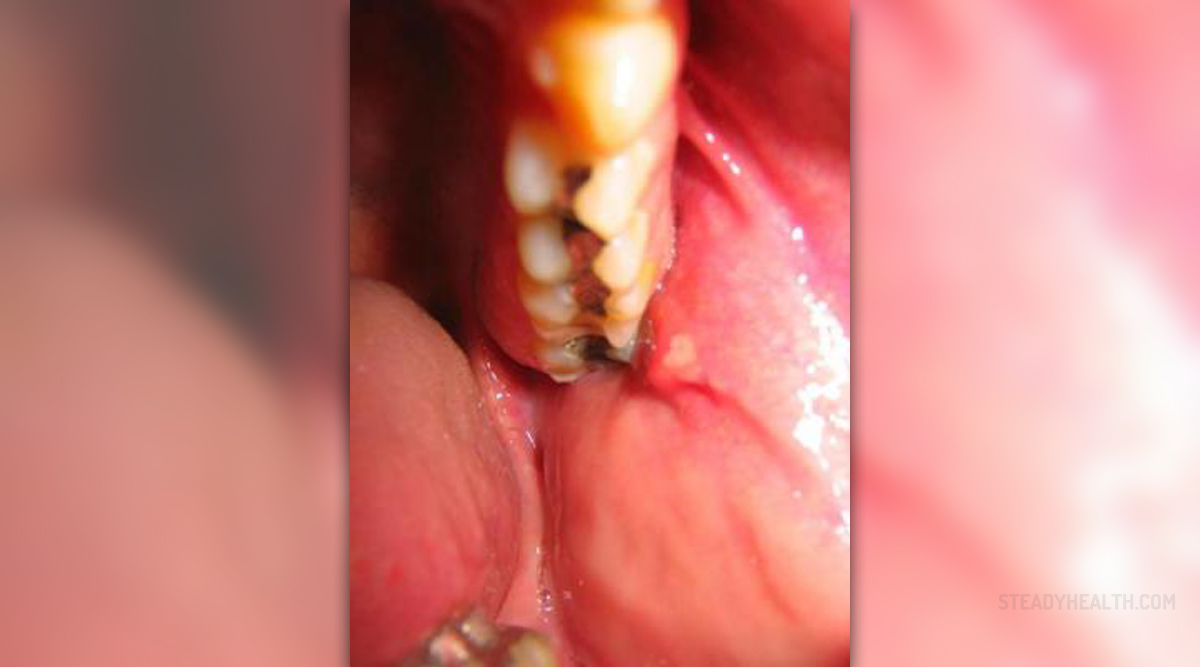
Gum disease is the infection of the tissues and the bone supporting the teeth. This kind of infection is one of the leading reasons of tooth loss in the United States. The disease can occur at any age and manifest in various health problems, from bad breath to serious conditions like pain and tooth loss. The disease is usually accompanied by the swelling, soreness and infection of the tissues, and it comes in two different types: as gingivitis or as a periodontal disease.
Gingivitis
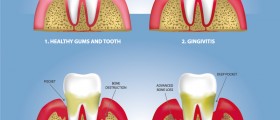
Gingivitis is a non destructive periodontal disease that develops as a response to bacterial plaques formed on the surface of the teeth and gums. This is a serious health concern as the untreated gingivitis commonly progresses to periodontitis, a destructive gum disease. Gingivitis usually manifest in the inflammation of the gum tissue, involving swollen gums, bright, red or purple in color, bleeding and tender or very painful to the touch. The gums usually bleed after brushing, which doesn’t occur if the gums are completely healthy. Patients with gingivitis usually have problems with bad breath.
This disease is usually caused by bacterial plague. Bacteria accumulate in the small spaces between the teeth, producing chemicals and toxins that can provoke an inflammatory response in the gum disease. The only way to prevent this from happening is through regular oral hygiene that includes brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash with antiseptic and anti-plaque properties.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the periodontium, the tissues that surround and support the teeth. The condition is characterized by the progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth. In most severe cases, this disease leads directly to the loss of teeth. The disease is caused by microorganisms that grow on the tooth’s surfaces. The immune system reacts to the presence of these bacteria, causing the inflammatory response in the gums. Symptoms usually include redness and bleeding of the gums while brushing or using dental floss. Recurring severe swelling of the gums is also common. Patients usually have a very bad breath and characteristic metallic taste in the mouth. Receding gums are also common, resulting in apparent lengthening of the teeth. Most of the patients will develop deep pockets between the teeth and the gums, which additionally compromises dental health, as the bacteria enter the pocket causing the inflammation and increasing the risk of developing abscess. At the later stage of the disease, teeth can become loose and fall out. Regular dental hygiene is, again, the only way to prevent periodontitis from occurring.





-Disease-Cause-A-Stroke_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...