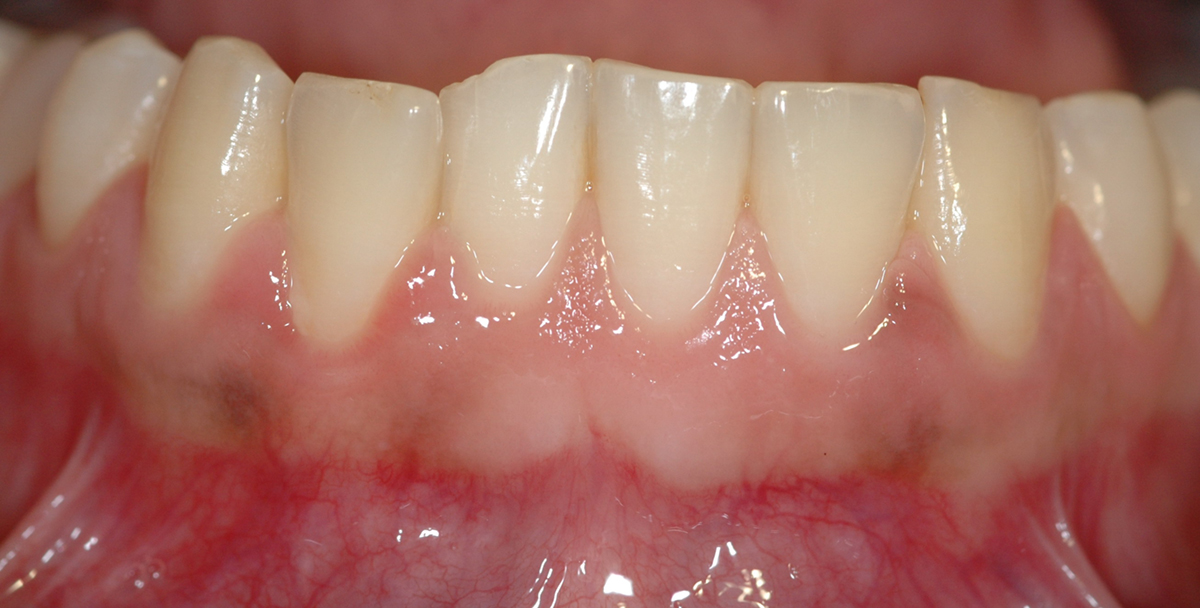
Recent studies show that over 50% of the Americans over 13 years-old suffer from some form of gum disease. Gum diseases usually develop as a response to profuse formation of bacterial plaque. If not treated they may lead to periodontal disease, tooth decay, serious damage to bone and even a tooth loss. However, gingivitis is preventable and curable by thorough removal of plaque, improved daily oral-hygiene habits, a proper diet, and nutritional supplements.
Causes
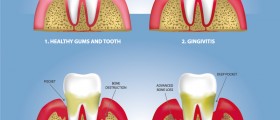
Gum disease occurs as a combination of many factors. The most common causes are bad oral hygiene, low nutrition diet, certain medical conditions, birth control pills or exposure to toxins (especially tobacco, smoke and certain drugs). Plaque-induced gingivitis is the most widespread type of gingival diseases. Bacterial plaque and food particles accumulate along the gum line and release toxic chemicals causing the inflammation of gums as well as the swelling of gingiva. This may often lead to formation of pseudo pockets.
Symptoms
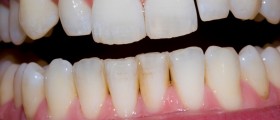
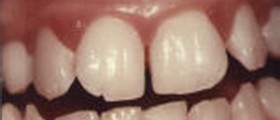
Affected gums are often swollen and reddish or purple, may feel sore or appear puffy. One of the earliest signs pointing out to gum disease is blood on the toothbrush or floss. If teeth appear longer because of the gums shrinking away, or if they are loose and sometimes fall off, than symptoms may indicate more severe problems (such as periodontal disease) and require immediate attention.
Risks
Untreated gum disease is clinically proven to be connected to heart disease, clogged arteries, stroke, premature birth, and diabetes. People with gum disease are twice as likely to die of a heart attack, ant three times as likely to have a stroke. Women suffering from gum diseases are up to seven times more likely to have preterm deliveries.
Prevention and treatment
Brush and floss are main tools to fight gingival diseases. Good mouth hygiene will prevent decay and infection to the teeth and gingiva. Patients should use brush and floss on a regular basis and rinse the mouth with saltwater instead of regular water.
Diet rich in vitamin C will help in preventing gum disease to the highest degree. Vitamin C helps body to produce healthy connective tissue that holds teeth in their openings. Vitamin B is also essential because it contains folic acid. All of the mouth surfaces, including gums, use large amounts of folic acid to stay healthy. Good sources of vitamin B vitamin are green leafy vegetables and brewer's yeast. Co-enzyme Q10 is an antioxidant nutrient essential for cell growth and recovery of the gum tissue.
Other supplements important for healthy gums are vitamin A (and beta-carotene), zinc, vitamin E, selenium, and flavonoids. The flavonoids are found in bilberry, hawthorn, grape seed, and green tea, and in many fruits and vegetables.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...