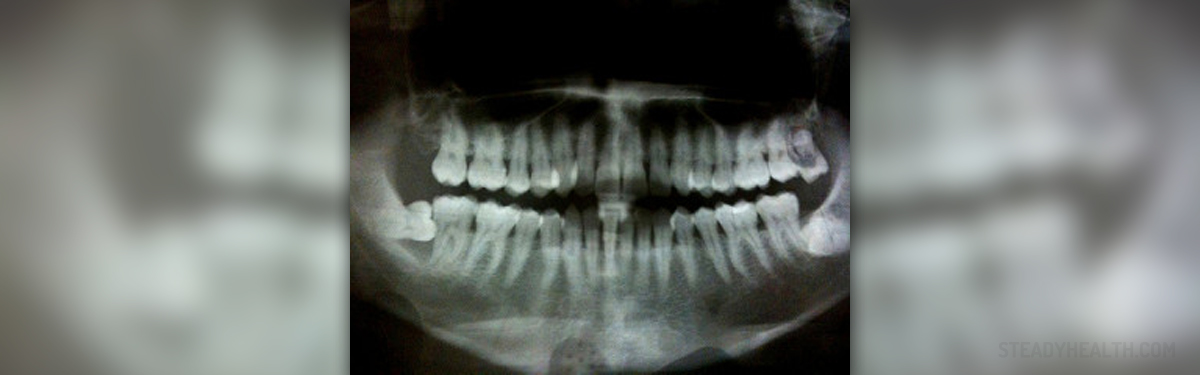
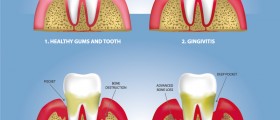
Signs and symptoms of chronic periodontal disease
Chronic periodontal disease doesn’t cause many of the symptoms at the early onset. In many cases, patients seek treatment only when the disease makes some serious progress and endangers the oral health in general. One of the primary symptoms of chronic periodontal disease is redness of the teeth and bleeding while brushing or using dental floss. In some cases, patients may experience bleeding from the gums even while chewing hard foods. Recurrent swelling of the gums is also a symptom of chronic periodontal disease. People affected with this disease usually have very bad breath and may have a persistent metallic taste in the mouth. In more advanced stages, gingival recession is present and appears as lengthening of the teeth. This occurs when the roots of the teeth become exposed as a result of the loss of gum tissue. Deep pockets may form between the teeth, and the gums and teeth may become loose or even fall out.
Prevention of chronic periodontal disease
Chronic periodontal disease is preventable in many cases. First and the most important step in prevention is to maintain a good oral hygiene. Teeth should be brushed properly at least two times per day and for at least three minutes. Proper brushing should be followed by flossing. An antibacterial mouthwash is also recommended, to help against the accumulation of plaques. In addition, people should lead a healthy lifestyle and eat a well balanced diet. A lot of vitamin C is highly recommended against gingivitis and periodontal diseases.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...