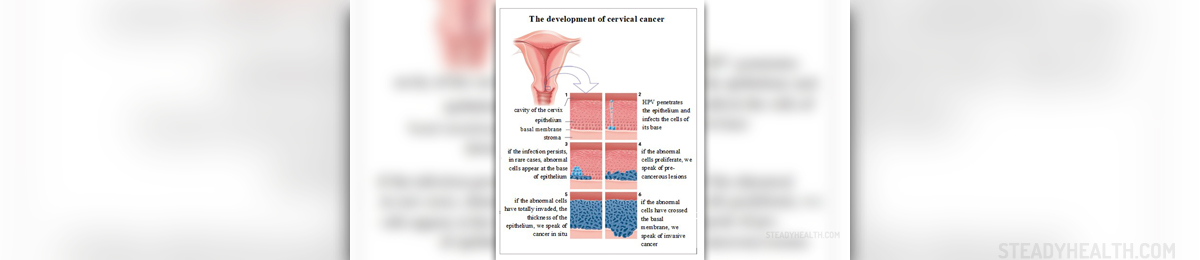
Cervical Cancer - Overview
Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor of the cervix, a part of the uterus. The very presence of the tumor can lead to vaginal bleeding but this one as well as other symptoms and signs of the disease usually occur in later stages of the disease, once the tumor has advanced. The most efficient treatment for cervical cancer is surgery and the best results and survival rates are expected if the disease is treated in early stage. Advanced stages of cervical cancer apart from surgery require radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Cervical cancer can be easily diagnosed with a simple screening test called Pap smear. Even potentially precancerous lesions of the cervix can be identified on time. This is why Pap smear is routinely used in women of all ages during regular gynecological exam. Almost all cases of cervical cancers are caused by previous infection with human papilloma virus (certain types of the virus).
Stages of Cervical Cancer
The very stage of cervical cancer provides with information on how far has the tumor spread. The stage of the disease represents crucial information in determining which treatment is going to be applied. There are 4 stages of cervical cancer and most of them are further divided depending on which structure has been affected.
Stage 1 cervical cancer refers to a tumor that is located in the cervix of the uterus. In stage 1 of cervical cancer the tumor is restricted to the cervix. So the tumor has not affected the nearby structures or has spread to the surrounding organs. The disease is limited and best treated in this particular stage of the disease.
Stage 2 cervical cancer features with spread of the tumor to the surrounding tissues. Namely, the cancer starts to spread outside the neck of the uterus and affects the top of the vagina and it also affects certain tissues around the cervix but it does not affect the muscles or ligaments of the pelvic wall.
In stage 3 cervical cancer the tumor affects the structures in the pelvic area. It usually grows into the lower part of the vagina and the muscle and ligaments of the pelvic wall are affected as well. Stage three also included spread of the tumor to the ureters.
And finally, stage 4 cervical cancers, also known as terminal stage of the disease, features with spread of the tumor to other body organs. The tumor usually spreads to the rectum and the bladder which are next to the uterus. Furthermore, it may also give metastases to distant organs such as lungs. All on all, terminal stage of the disease leads to inevitable death and the patients may be only treated palliatively.



_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...