Ear Drainage Facts
This condition is very common with children and is this mostly connected with age. Nevertheless, ear drainage may affect adults as well. Whichever group it affects, this phenomenon is most closely connected to an underlying ear infection. The following lines will provide further information about ear drainage regarding possible causes, symptoms and treatment. Thus, if you desire to learn how to react in case you get in contact with this condition, read on.
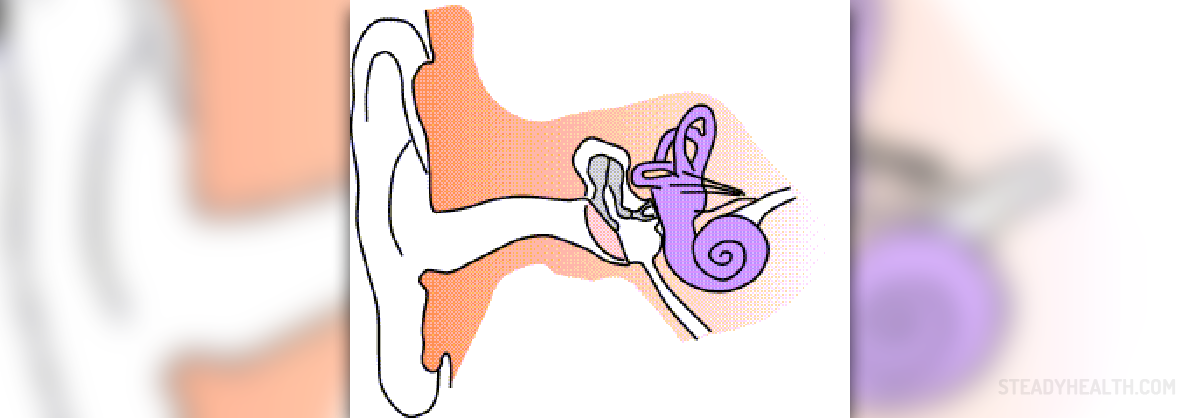
- Acute discharge in people without longstanding ear problems or a weakened immune system is usually not dangerous and is typically due to an external ear infection or a perforated eardrum resulting from a middle ear infection.
- People who have chronic ear symptoms or any symptoms besides ear discharge (particularly any neurologic symptoms) should be evaluated by a specialist.
- Some people with chronic otitis media develop a noncancerous (benign) growth of skin cells in the middle ear (cholesteatoma ) that can cause discharge. Although a cholesteatoma is noncancerous, it can cause significant damage to the ear and nearby structures. In severe cases, a cholesteatoma may lead to deafness, facial weakness or paralysis, and complications with the brain such as an abscess and other infections.
- During the physical examination, doctors focus on examining the ears, nose, throat, and neurologic system. By examining the ear canal with a light, doctors can usually diagnose perforated eardrum , external otitis , foreign object , and other common causes of ear discharge. Other findings suggest the diagnosis.
- If the cause is not clear, doctors usually do a formal hearing test (audiometry) and computed tomography (CT) or gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). If abnormal tissue is present in the ear canal, a tissue sample (biopsy) may be taken. Sometimes culture swabs are taken of the drainage to identify infection.
Reasons behind Ear Drainage in Adults
There are several different causes of this phenomenon. They all manifest to certain type of fluid, coming out of a person's ear. If this fluid is watery, it is most probably a sign of an ear infection, taking place behind the ear drum. On the other hand, drainage in the form of blood, most likely indicates an injury like an ear drum perforation, ear wall damage or similar. Additionally, there are several other conditions which are capable of triggering ear drainage in adults. Various infections, injuries of the ear interior and many other complications all may lead to the onset of ear drainage.
The main key to diagnosing the cause behind specific ear drainage is the expelled fluid itself. Namely, different smell, consistency, thickness, color, and other properties, all indicate different conditions having ear drainage as a symptom.
As for ear infections, these are extremely painful. The sufferer may experience pain upon touching, or constant pain, with ear drainage varying in color, being transparent, white or yellow, smelling extremely unpleasantly. Different particles can be present in the fluid as well. Headaches are quite common during these infections. Direct traumas to the ear drum or some other ear parts, as mentioned above, result in blood drainage and extreme pain. Hearing impairment and/or loss are also possible.
The worst case scenario would involve an ear tumor, which produces a bright red or yellow ear secretion. Nevertheless, the most common reason behind this condition is excessive ear wax. Sometimes, while we move our jaw or perform similar actions, our ear wax gets expelled, resulting in the dark yellow, scaly and sticky discharge. However, this is completely normal and usually caused by poor ear hygiene. All in all, color and smell are main clues of the type of the problem you are facing once you experience ear drainage. Thus, if your discharge has a foul smell, or has unwanted colors mentioned above, let alone comes hand-in-hand with pain and discomfort, seek medical attention as soon as possible.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...