There are a large amount of drugs that can cause damage to the respiratory system. The number is said to be around three hundred and fifty. Awareness of the growing number of drugs that can cause such problems is increasing.
Examination
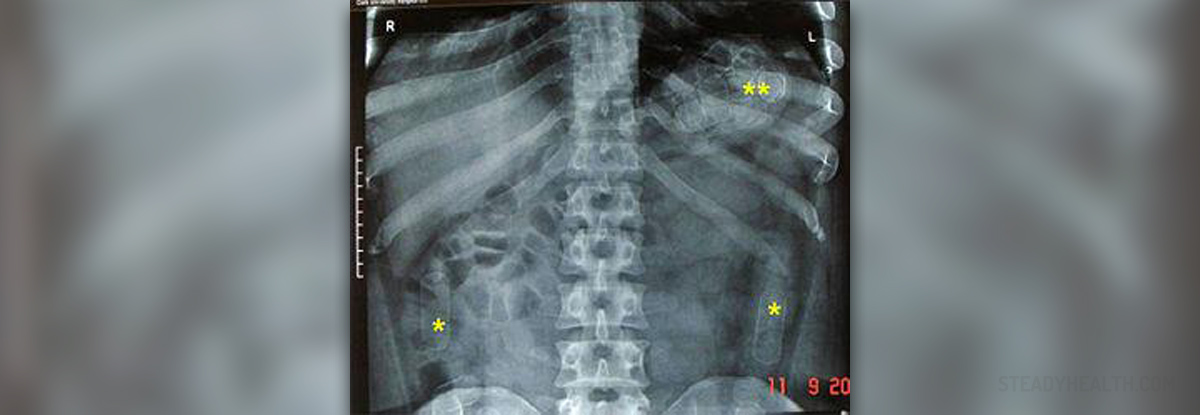
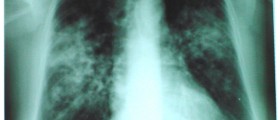
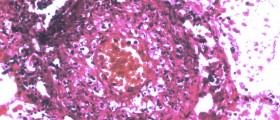
Chest radiography is often used to examine the options available to those suffering from problems of this kind. In some cases, high resolution computed tomography and radionuclide imaging might be used to detect lung toxicity. The main problem with this type of examination is that toxicity of the lungs has something of a non-specific appearance. Lung toxicity resulting from drug use often appears in a similar fashion to other lung diseases.
Toxicity
Up to ten per cent of patients taking busulfan will be affected by this problem. Busulfan toxicity can be recognized by the presence of diffuse linear opacities, which can be similar in appearance to pneumocystitis, pneumonia and interstitial leukemic infiltrates.
Bleomycin might occur in the case of the administration of a dose larger than 300 mg. Age, radiation therapy and a high concentration of oxygen are often associated with toxicity of this type. This might be indicated by subpleural linear and/or nodular opacities at the base of the lungs.
Ethotrexate lung toxicity is another type of toxicity that might occur. This is usually self-limiting and is often associated with blood eosinophilia. Visible changes will include linear and/or reticulonodular opacities.
Nitrofurantoin toxicity can be acute or chronic, though the former is more common. Fever and eosinophilia might occur. With this type of toxicity, bilateral basal interstitial opacities might be observed.
Other types of toxicity can occur through the use of heroin, propoxyphene or methadone. In this case, aspiration pneumonia might occur. It is also possible to overdose on Aspirin, which can lead to pulmonary edema.
A type of therapy that is associated with these types of toxicity is amiodarone therapy, particularly with regard to alveolar and interstitial infiltrates. Lung consolidation might have an increased density as a result of the iodine content. In the case of drug or radiation-induced lung disease, ground glass opacity might be observed. This type of opacity is easily identified using high resolution computed tomography than with radiography. This type of opacity is often observed in those with early diffuse pulmonary infiltrative diseases.
Antibiotics can also lead to an increase in toxicity. Amongst these antibiotics are drugs such as nitrofurantoin, amphotericin B, sulfonamides and sulfasalazine. Lung diseases related to antibiotics include interstitial pneumonitis and fibrosis, hypersensitivity, ARDS and BOOP.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...