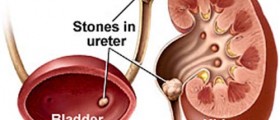
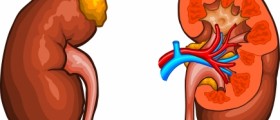
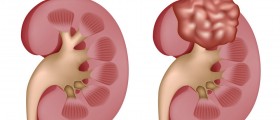
A kidney stone is basically a solid mass of tiny crystals. There can be more than one stone in the kidney or ureter at a given time. Kidney stones are also known as renal calculi, or nephrolithiasis.
Causes of Kidney Stones
When the urine contains too much of a particularly harmful substance, this might lead to the formation of a kidney stone. A major risk with regard to kidney stones is dehydration. This condition is common and can lead to swelling of the kidneys and severe pain. Those who have suffered kidney stones once are generally vulnerable to a recurrence of the condition later in life. Certain kinds of kidney stones are hereditary, while others occur as a result of bowel disease, ileal bypass, or renal tubule defects.

The exact cause of the kidney stone will depend on which type of stone is the problem. The most common type of stone is calcium stone. These stones occur mainly in men aged twenty to thirty and can be recurrent. Calcium stones occur as a result of calcium combining with other reactive substances.
Those who suffer from cystinuria might develop cystine stones. This is normally a hereditary condition that is equally prominent in men and women. Struvite stones might occur in women with urinary tract infections. Stones such as this can become large and might lead to kidney, ureter or bladder blockage. Another type of kidney stone that might occur is the uric acid stone. This type of stone occurs often in conjunction with chemotherapy or gout.
- Urinary calculi can be induced by a number of medications used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Drugs that induce calculi via this process include magnesium trisilicate; ciprofloxacin; sulfa medications; triamterene; indinavir; and ephedrine, alone or in combination with guaifenesin.
- Magnesium trisilicate; ciprofloxacin; sulfa medications; triamterene; ephedrine, alone or in combination with guaifenesin; and indinavir may induce calculi via urinary supersaturation. Eliminating such calculi usually involves discontinuation of the medication and initiation of an alternative therapy.
- Loop diuretics, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and abused laxatives can cause metabolic abnormalities that facilitate the formation of stones. Correction of the metabolic abnormality can eliminate or greatly attenuate stone activity.
Symptoms
A major symptom of kidney stones is severe pain. This pain might be sudden and felt in the belly, side, groin or testicles. Abnormal urine color, urinal blood, chills, fever, nausea and vomiting are other potential signs of the presence of kidney stones. Severe pain might require the use of narcotic pain relievers. The abdomen or back can be tender.
Treatment
Treatment will focus on symptomatic relief. Depending on the type of stone, treatment will also vary. Severe symptoms might lead to hospitalization. After the passing of the stone, the urine should be strained. The stone should also be saved and subsequently tested.
One should also try to drink around six to eight glasses of water each day. In some cases, the intravenous intake of fluids might be required. Some medications exist that can help to break down the stones are available, including allopurinol, antibiotics and diuretics.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...