Interstitial lung disease is the general term for a group of the lung diseases that are characterized by the progressive scarring of the lung tissue. Interstitial lung disease leads to difficulty in breathing due to which the person does not get sufficient oxygen into the blood stream. In the majority of cases, when the scarring of the lung tissue occurs, it cannot be cured, but certain medications can slow the damage of this disease to the lungs.
Symptoms of interstitial lung disease
Since interstitial lung disease includes several lung disorders, the symptoms may vary depending on the disorder and on severity of the disorder. However, the most common symptoms of all lung disorders are dyspnea and dry cough. Dyspnea is a medical term for breathlessness, which is the most severe during or after physical activity. Many people tend to mistake these two symptoms for the symptoms of some other disorder, such as asthma, obesity, aging or smoking.
Since the interstitial lung disease is progressive, the symptoms aggravate over time. Breathing problems become more obvious and wheezing, as well as pain in the chest appear. One of the warning signs of the interstitial lung disease is the curving of the fingernails over the tops of the fingertips.
Causes of interstitial lung disease
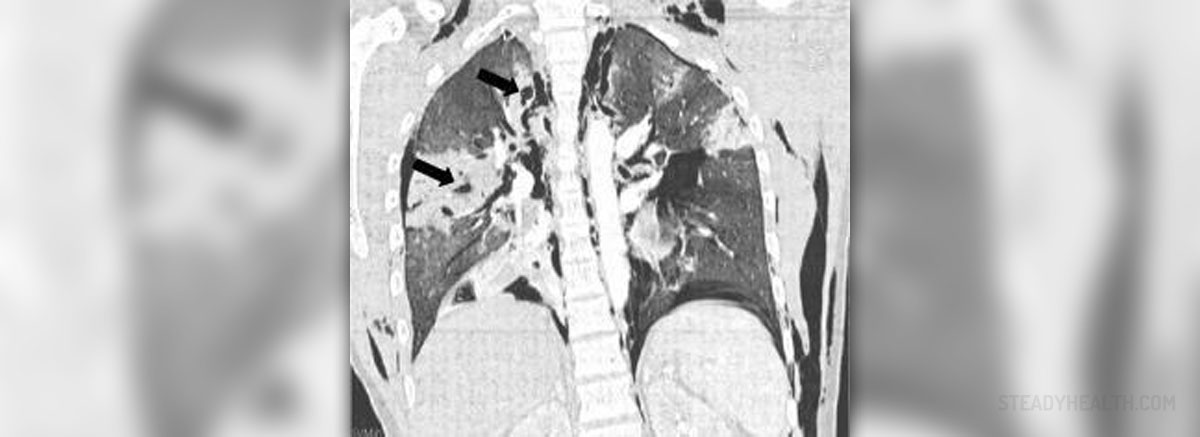
The bronchi are major airways through which the air travels to the lungs. In the lungs, the bronchi make the network of bronchioles, which are smaller airways. These bronchioles end in alveoli, which are small air sacs. The alveoli are important since the capillaries are in the walls of them. Here, oxygen is added to the blood and carbon dioxide is removed.
One of the causes for the occurrence of interstitial lung disease is the scarring of tiny air sacs. When the alveoli are inflamed, the tissue that surrounds them becomes scarred and thickened. As a consequence, the alveoli are not flexible anymore and cannot expand and contract easily. Therefore, the breathing becomes difficult and oxygen hardly enters the bloodstream through the thickened walls. Another cause for the incidence of interstitial lung disease is abnormal healing response. When an injury to the lungs happens, it causes abnormal healing response. Normally, the body usually produces the tissue to repair the damage. However, sometimes it happens that the body produces excess scar tissue that interferes with lung function.
Interstitial lung disease may also be caused by many viral or bacterial infections, radiation and exposure to many occupational and environmental factors, such as pollutants and toxins. Furthermore, many medicines can lead to the damage of the lungs, especially those medicines that are used in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders.








,-Asthma-And-Anxiety_f_280x120.jpg)





_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...