Fibrosing alveolitis is a chronic lung disease that belongs to a group of diseases called interstitial lung diseases. Fibrosing alveolitis is also called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis.Fibrosing Alevolitis Introduction
Fibrosing alveolits is the condition featured by inflammation of the lungs that results in thickening and fibrosis along the alveoli walls. The exact cause of fibrosing alevolitis is still unknown. Fibrosing alveolitis is a serious disease in which lung function gradually decreases. A form of fibrosing alevolitis known as Hammond-Rich syndrome particularly responds poorly to treatment.
The term cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is mainly used for cases in which lung histology reveals pathological changes called “usual interstitial pneumonitis” (UIP).
The number of cases of fibrosing alveolits appears to be rising and has doubled between 1990 and 2003. However, it is not yet clear why. Also, an American study has shown that mortality rates have increased from 1992 to 2003.
Fibrosing alveolitis is believed to be triggered by exposure to airborne agents such as asbestos, silica, coal dust, metal alloys and other substances. Smoking is also one of the main risk factors. Pigeon breeding and contaminated ventilation systems are other environmetal factors. Finally, fibrosing alveolits can occur as a side effect of amiodarone.
Middle aged people (50 years and older) are most commonly affected by fibrosing alveolits. Also, men are more susceptible to the condition than women. In some patients there has been seen genetic predisposition to fibrosing alveolitis but this is not common.
Signs and Symptoms of Fibrosing Alveolits
The primary symptom of fibrosing alveolits is shortness of breath with exertion. Dry, unproductive cough is common too. Half of the cases present flu-like symptoms, fatigue and weight loss. Symptoms of fibrosing alveolits also include muscle pain and skin rash.
As the disease progresses shortness of breath occurs even at rest. Right heart failure is seen too. Change in the shape of fingernail and toenails as well as skin color changes (cyanosis) are present as well.
Diagnosis of Fibrosing Alveolits
Since fibrosing alveolits does not have specific symptoms a doctor must rule out other conditions that cause the same or similar symptoms. These conditions include heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sarcoidosis, pulmonary embolism, lymphangitis carcinomatosis and extrinsic allergic alveolitis.
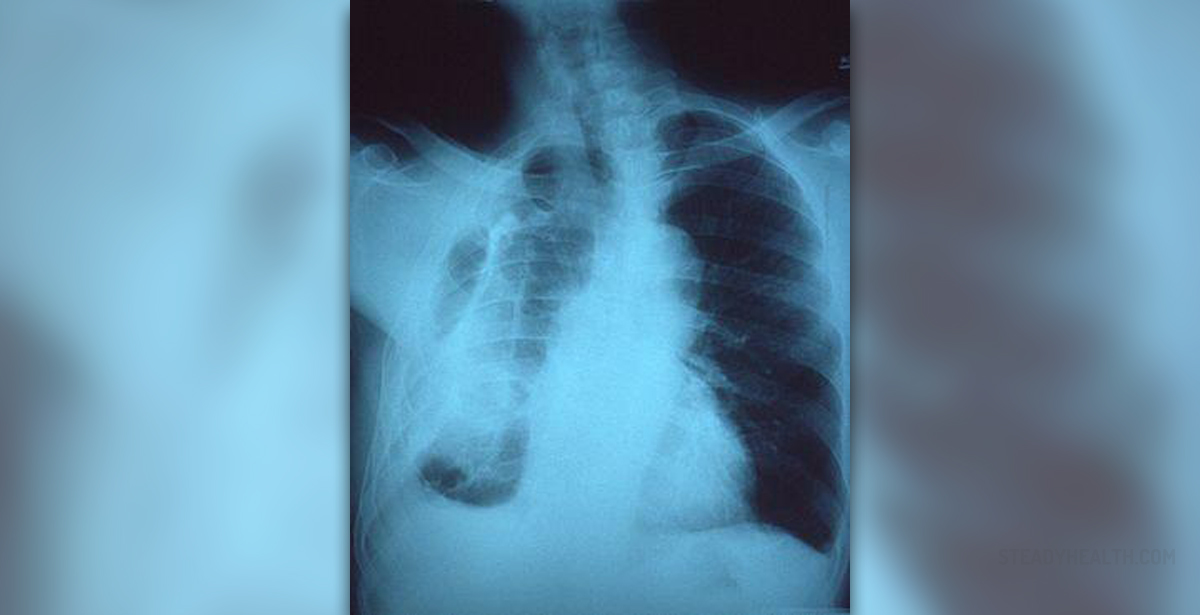
For this purpose the doctor will order laboratory tests such as blood test that measures levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood and lung function test. Chest x-ray and high resolution CT scan are also used to look scar tissue in the lungs.
Finally, lung biopsy is used to confirm the diagnosis. Both open lung biopsy and bronchoscopy may be required.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...