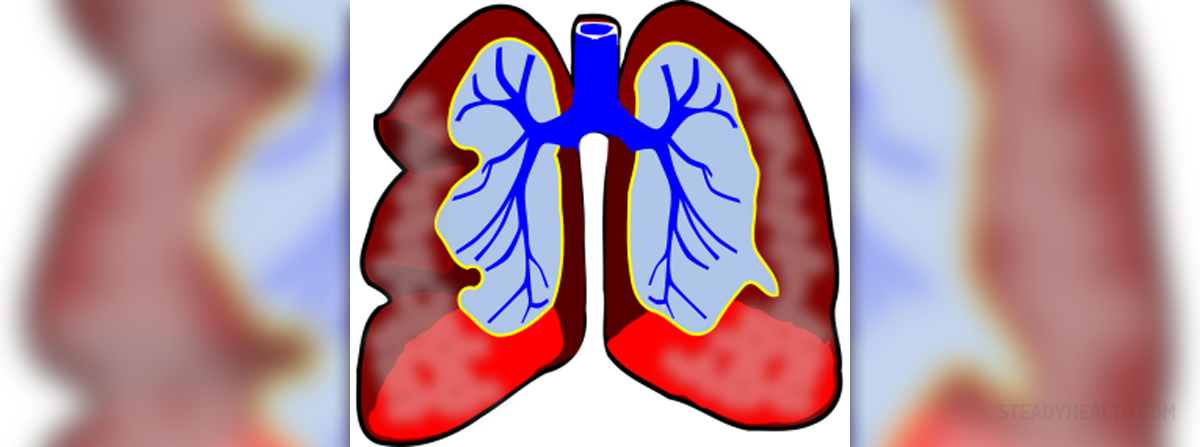
Inflammatory lung diseases
These ailments are also known as the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Inflammatory lung diseases include a wide range of illnesses such as asthma, emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Emphysema is a long-term progressive disease that usually causes shortness of the breath. Asthma, on the other hand, presents a chronic disease of the airways distinguished by changeable and returning symptoms. This type of a lung disease is characterized by chronic inflammation and reduced ability to breathe. Inflammatory lung disease may even put additional pressure on the heart, and affect the patient’s life on several levels, by making it hard to engage in exercise, hard work, or any other activity that requires heavier breathing.
Obstructive lung diseases
This is a type of lung disease characterized by some type of the airway obstruction. Main obstructive lung diseases include chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis (dilation and scarring of airways), asthma, emphysema or bronchiolitis (inflammatory scarring and bronchiole obliteration). Persistent and severe infections, air pollutants or tobacco smoking typically causes these diseases. However, they may occur as autoimmune disorders (asthma, for example).
Restrictive lung diseases
These diseases form a separate category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that manifest in restriction of the lung expansion. Therefore, people suffering from restrictive lung diseases have increased work of breathing, inadequate ventilation and, consequently, severely decreased oxygenation. Pulmonary fibrosis, or scaring of the lung of the tissue, usually causes changes in the lungs lessening their normal breathing capacity. In many cases, restrictive lung diseases have no known cause, but they can sometimes develop as a result of asbestos exposure, as a side effect of radiation, certain drugs, or consequence of some other disease such as rheumatoid arthritis. Sometimes, restrictive lung disease occurs because of the injury to the lung, or as a birth defect in the lungs of a baby born prematurely.
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000066.htm
- medlineplus.gov/lungdiseases.html
- Photo courtesy of Clker-Free-Vector-Images by Pixabay: pixabay.com/en/lungs-human-diagram-respiratory-39981/










,-Asthma-And-Anxiety_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...