
Definition of Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease is actually an umbrella term which is commonly used for a group of different types of disorders which are mostly associated with progressive scarring of the tissue located inside the lungs. In most cases of interstitial lung disease, the biggest problem with the aforementioned scarring of the lung tissue is the reduced ability to breathe which leads to reduced amount of oxygen in the patient’s bloodstream. Another big issue with this scarring is that once it occurs it cannot be reversed. There are several different types of medicaments which can be used to slow down the damage and lung transplants are another option but it is actually a very tricky one. This type of medical condition is commonly characterized by certain symptoms such as dry cough and shortness of breath which often gets further aggravated by exertion. Interstitial lung disease may sometimes lead to certain life threatening medical conditions and complications and those include respiratory failure, right ventricle heart failure and high blood pressure in the lungs which is medically referred to as pulmonary hypertension.
Statistics on Interstitial Lung Disease
According to various scientific studies, the interstitial lung disease commonly affects men much more than it affects women, but it is very hard to follow any statistics on this medical condition since not all cases are carefully noted. It has been estimated that 15% of all respiratory physician visits in the United States occur mainly because of interstitial lung disease. In numbers, it adds up to 100,000 American citizens suffering from this disease each year. Only 15% of cases of interstitial lung disease can be considered as immediate causes of death. This medical condition ends in death only in less than 50 percent of all cases.
Causes of Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease can be triggered by a large number of different causes and factors, but the big problem is that in most cases the exact cause is very hard to pinpoint. Unfortunately, once a person notices any symptoms, the damage commonly already occurs so it is of utmost importance to pay a doctor a visit as soon as possible. An early, proper diagnosis is the only way to proper treatment methods which sometimes may even save one’s life, depending on the severity of the condition and the damage it has caused. In normal conditions, the human body is able to repair the damage to the lung tissue simply by generating new tissue, but in cases of interstitial lung disease a sort of abnormal healing response occurs and it leads to the scarring and thickening of the tissue which surrounds the air sacs. This is why oxygen cannot pass into the bloodstream the way it should. There are certain types of medical conditions which may lead to the development of interstitial lung disease and the most common ones include scleroderma, sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosis. Unfortunately enough there are also a large number of different types of medications which can be held responsible for the damage of the lung tissue. Antibiotics such as sulfasalazine and nitrofurantoin, heart medications such as propranolol and amiodarone and chemotherapy drug such as cyclophosphamide and methotrexate are the ones which are usually associated with the scarring of the lung tissue. People who receive radiation therapy as a treatment for the breast cancer or lung cancer sometimes also experience lung damage, but there are certain factors which determine the severity of the damage and those include the presence of some underlying lung disease, the presence or absence of chemotherapy in the treatment plan, the total amount of radiation administered and the size of the portion of the lung exposed to the radiation treatment. The lung tissue may also be damaged due to the long term exposure to various different types of pollutants and toxins. The most common ones include bird and animal droppings, grain dust, asbestos fibers and silica dust. There are also other factors and causes which may trigger the onset of lung tissue damage and interstitial lung disease and those include excessive exposure to therapeutic oxygen, smoking and simple effects of the process of aging.
Management of Interstitial Lung Disease
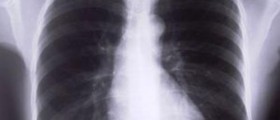
In order to properly diagnose the medical condition, the doctor needs to be well informed on the symptoms which are present, any treatments for other medical conditions, any supplements taken in the recent time, the patient’s occupations and any chronic lung diseases in the patient’s family. There are certain imaging tests which need to be conducted and those include chest X-ray, computerized tomography and echocardiogram. Further pulmonary function tests commonly include the ones called spirometry, oximetry and exercise stress test. Lung tissue analysis may be required in some cases, and the ways of obtaining a tissue sample include bronchoscopy, bronchoalveolar lavage and surgical biopsy. The treatment options for those who suffer from interstitial lung disease include corticosteroids, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation and surgery. One needs to stop smoking and also to establish a healthy and well balanced diet.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...