Information on Thumb Joint Pain
This medical condition can trigger quite a few problems because the thumb joint is one of the most frequently used joints in the human body. Painful sensations in the thumb joint may be associated with further medical complications, such as tingling sensations in the fingers and the palm, and they may also cause numbness in the palms.
Since this medical condition involves severe painful sensations, it may be hard to hold things or grip objects. In most cases, the painful sensations are usually accompanied by stiffness and swelling of the affected area. Pain in the thumb joint can be triggered by numerous different factors and causes.
Causes of Painful Thumb Joint
The most common cause of painful sensations and swelling of the thumb joint are injuries that occur due to bruising. Other types of injuries may include strains and sprains, which may cause the wrist and the fingers to become immobilized. When the tissue in the surrounding area gets irritated and inflamed painful sensations in the thumb joint occur.

This condition is medically referred to as tendonitis, but it usually gets developed due to the process of aging. Fractures are another type of injury that may be affiliated with painful sensations in the thumb joint. Another medical condition that may be affiliated with painful sensations and swelling of the thumb joint is referred to as bursitis.
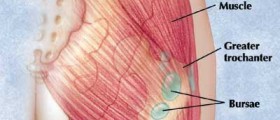
Bursa is a sac that gets filled with lubricating fluid that is normally located between the different tendons, bones, muscles, and skin. This fluid is beneficial in decreasing the irritation, rubbing, and friction which occur during numerous different motions. Any type of injury that may affect the bursa usually causes bursitis.
Bursitis may be affiliated with palm injuries and the process of aging. Another cause of bursitis may be repetitive overuse of the thumb joint. Another common cause of painful sensations, swelling, and stiffness in the thumb joint is the medical condition known as arthritis. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis.
- The prevalence of basal thumb arthritis increases with age and is seen predominantly in postmenopausal women. The female:male ratio is 6:1. No conclusive environmental or genetic factors that lead to the expression of this disease have been identified.
- We found a strong association between excessive basal joint laxity and the development of premature degenerative changes. Ligamentous laxity is common in young women. Repeated loading of subluxed joints in the 20s, 30s and 40s may be the reason why one third of women >50?years show some radiological evidence of degenerative change.
- Typically, patients have pain localised to the base of the thumb, often radiating to the thenar eminence and the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint. The pain in basal thumb arthritis is often activity related, particularly after excessive use involving forceful pinch. Daily activities such as grasping large objects, unscrewing jar tops, turning doorknobs and writing can exacerbate symptoms. As the arthritis progresses, pain may become constant. In addition to pain, weakness or loss of motion are commonly reported.
- A detailed history and clinical examination is all that is normally needed to clinch the diagnosis. Radiographs are helpful in staging the disease and for patient education, as discussed in the next section. Nerve conduction studies are recommended, if there are relevant sensory problems.
- The mainstay of initial treatment of basal thumb arthritis of any stage is activity modifications, rest, non?steroidal anti?inflammatory drugs, and thenar intrinsic and extrinsic muscle strengthening exercises.
- The indications for surgery in patients with basal joint arthritis are persistent pain and functional disability after failed conservative treatment in the compliant patient. Staging can then provide a rationale for the selection of reconstructive surgical options.
The basal joint is the one responsible for the pivoting motion, and it can cause wear and tear very easily. This can lead to arthritis, especially osteoarthritis. The cartilage of the basal joint gets damaged, and it leads to the rubbing of the bones against the joint which leads to painful sensations. The condition gets worsened by the process of self-recovery.
The condition cannot be cured, and the treatment always depends on the actual cause of the condition.



-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...