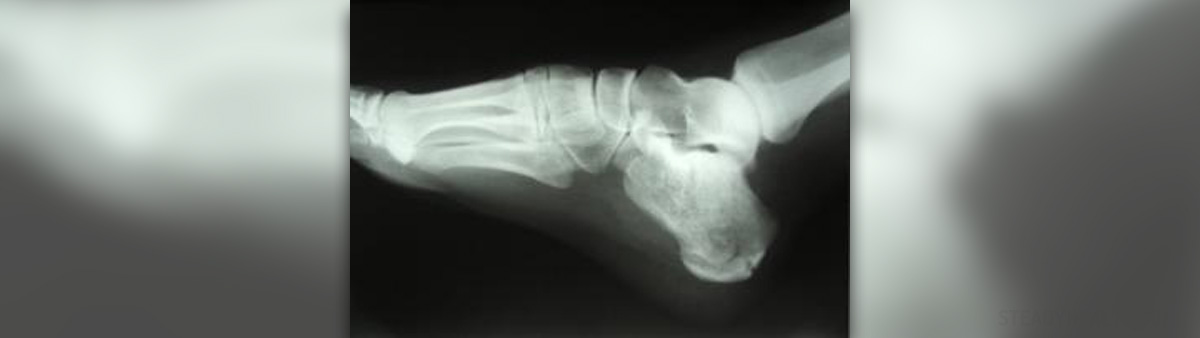
The calcaneus is a medical term for the heel bone. There are several muscles attached to the calcaneus. In case these muscles contract a pulling force it is exerted onto the bone. Apart from that, the bone is exposed to increased pressure during weight bearing activities. In case the pressure exerted on the bone exceeds certain levels, ther is increased risk for bone fracture. Increased pressure initially leads to bony stress reaction and if it lasts long enough or is repetitive it may eventually result in calcaneal stress fracture.
Causes and Presentation of Calcaneal Stress Fracture
This type of fracture is generally associated with excessive weight bearing activities (jumping, running etc). Furthermore, calcaneal stress fracture may occur in cases of a recent increase in activity or even change in training conditions.There are certain factors which may contribute to this particular fracture and they include poor foot posture, poor footwear, poor flexibility, muscle weakness, ankle joint stiffness and inappropriate or strenuous and excessive training especially if it is performed on hard/ uneven surface.
The main symptom of calcaneal stress fracture is pain which is most commonly felt on either the inner or outer aspect of the calcaneus. The pain tends to intensify with certain activities such as marching, running, jumping or landing. If the fracture is severe a patient can barely walk. The pain may also intensify during the night and if the injured area is touched.
Diagnosing Calcaneal Stress Fracture
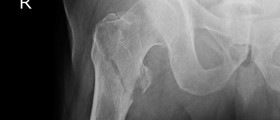
The injured area must be thoroughly examined. Definitive conformation of the fracture is achieved by X ray of the particular area. Even an MRI or CT scan may be required although the fracture was detected with a simple X ray.
Treatment for Calcaneal Stress Fracture
The cornerstone of the treatment for calcaneal stress fracture is rest. The rest must start immediately after the injury or after the fracture has been diagnosed. Any kind of weight bearing activity is strictly forbidden. Additional help is obtained from crutches and protective boot. This particular period when a patients is not supposed to engage in weight bearing activities lasts approximately 6 weeks. What follows is a gradual increase in weight bearing activities and physical therapy. A well experienced therapist will explain and teach the patient what exercises are the best for the recovery and how they are supposed to be performed.
The best results of rehabilitation are achieved with exercises that place minimal weight bearing forces to the affected bone. They include swimming, cycling and water running. Exercises are also supposed to be created in such manner to restore flexibility, strength, balance and function of the injured area.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...