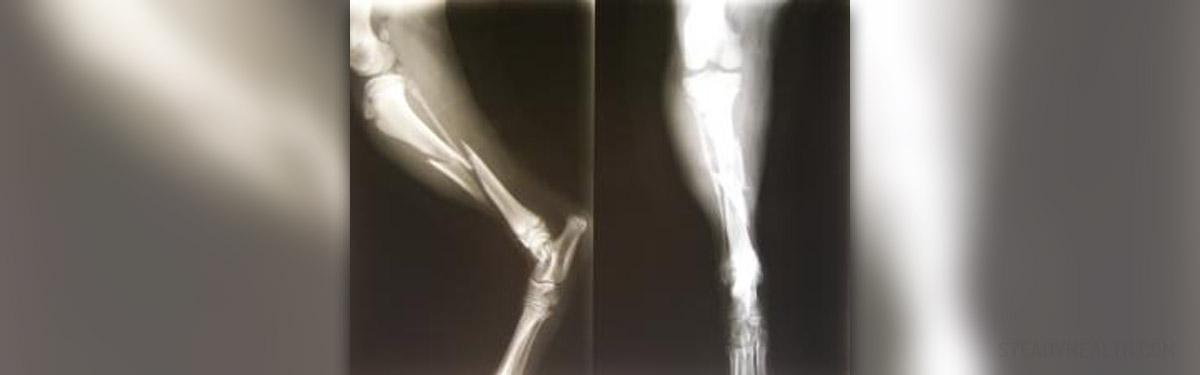
A comminuted fracture is a type of bone fracture that results in the presence of three or more bone fragments, sometimes splintering into many individual sections. A comminuted fracture is a serious type of fracture that results from severe physical trauma, and the treatment can be rather challenging, requiring surgical repair to offer patients the best chance of a full recovery. Due to multiple bone fragments, or in layman's terms, a rather well-shattered bone, there is an increased risk of complications after comminuted fractures.
Comminuted fractures can be classified into open and closed fractures. In open comminuted fractures, the bone fragments protrude through the skin, becoming externally visible. This carries a significantly increased risk of serious complications such as infections, as bacteria can easily enter such wounds. In case of close fractures, the bone fragments do not cause a tear to the skin. The skin is practically intact and the damage done in this type of comminuted fracture only affects the underlying tissues. This does not necessarily make them less damaging.
Causes and Symptoms of Comminuted Fractures
Comminuted fractures are typically associated with crush injuries. These kinds of fractures are rather common in elderly people. They are particularly predisposed to fractures due to the process of aging which causes structural changes in skeletal system, making it more susceptible to fractures and other injuries.
Furthermore, a comminuted fracture may occur in people suffering from primary or secondary bone cancer, osteogenesis imperfecta, osteoporosis, and other bone disorders. This particular type of fracture results from enormous force which typically occurs in car accidents and a fall from a great height.
Patients who have experienced a comminuted fracture complain about intense pain at the very site of injury. Soon after the injury the particular area becomes swollen, tender and warm to the touch. In open comminuted fractures, the bone fragments protrude through the skin and there may be bleeding.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Comminute Fracture
Once the patient has been admitted to the hospital or clinic, the doctor first performs a physical examination. The diagnosis is definitive once the injured bone is exposed to X-ray examination. Additional laboratory tests and CT scan of the injured area are usually required. After these examinations, patients are administered pain relieving medications.
The treatment for comminuted fracture includes surgical repair and fixing of the broken bone. It is essential to reconnect the broken bone fragments and then fix them with medical materials such as surgical nails, screws, plates or wires.
Once the injured area is cut open, the surgeon has insight in all surrounding structures. This way, he or she may look for possible damage to nearby tissue and perform suitable repair. Bone fragments are aligned with a technique called reduction. After the surgery the injured part is immobilized with a plaster, splint or fiberglass splint.
The fracture usually takes a long time to heal completely, so recovery time lasts beyond that of simple fractures. After the surgery all patients should be engaged in physical therapy. The goal of physical therapy is to restore the lost function of the broken bone and to strengthen the surrounding muscles. Complications such as infection at the site of fracture may only prolong the recovery time and require aggressive treatment with antibiotics.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...