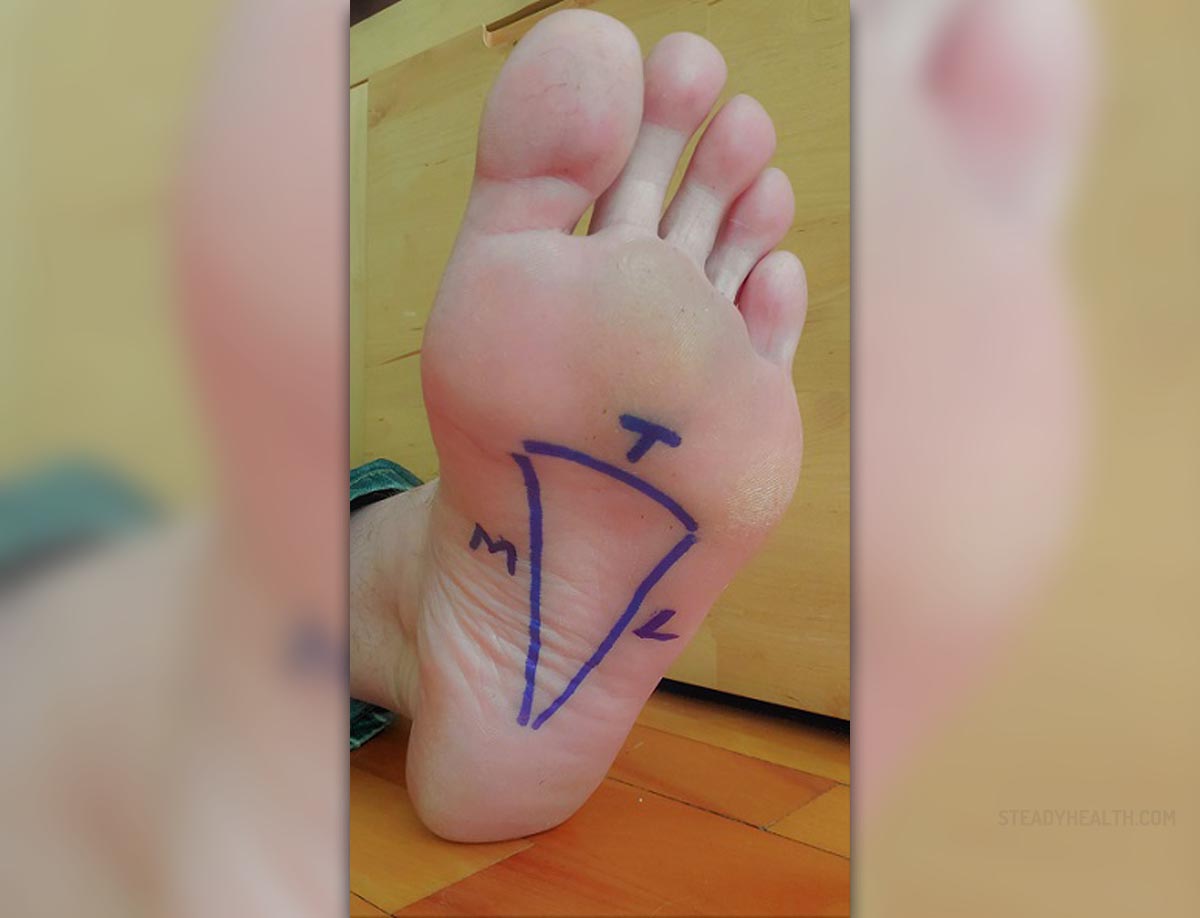
Human feet
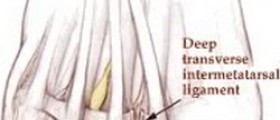
Human foot is a very complex. Each foot contains 24 bones, organized in two arches, one running the length of the foot, and other the width. Arches absorb impact force from walking, much like springs. Bones in the feet are held together by fitting into each other, much like a jigsaw puzzle, and are further supported with fibrous tissue (ligaments) and foot muscles together with a sinewy tissue known as plantar fascia.
Fat pads in this structure help to ease load of carrying body weight and to reduce impacts generated while walking. If something in this complex mechanism does not work right, arch pain will be the likely outcome.
Causes of arch pain
Most arch pain origins from muscle strain, ligament sprain, injury, fractures, poor alignment or tightness of structures.
Injury to the fascia can lead to an inflammatory response that causes pain. This is a frequent source of arch pain. Single or repeated stress (like when somebody steps on it) can cause damage to various foot structures. Injury to the bone that originates from a single blow or twist or repetitive stress can cause a stress fracture. Overstretched ligament fibers can tear.
Foot muscles can be injured by overloading, bruising, cutting. Certain repetitive movements that stress the arch can cause arthritis of the arch joints. Micro-trauma injuries appear when foot structures are continuously stressed to the point when injury appears, ie. when using shoes that absorb impacts badly, running on uneven surfaces or exercising too long and too hard.
Symptoms of arch pain
Pain in the bottom of the foot, in a specific or wider area, is usually associated with strains on the plantar fascia, and it can be increased or decreased by stretching the arch. Pain usually fades when the foot "warms up" in mild cases of fascia inflammation, but can increase with prolonged use.
Pain that can be pinpointed to a specific area, in motion or at rest, is indicator of a problem in that specific area. In example, sprain is indicated by point tenderness and looseness in a joint, and fracture can trigger severe point tenderness in the area of the fractured bone.
Direct force injury causes bruising, but severe pain, swelling, discoloration or alterations in gait may point to a serious damage. Complexity of feet structure requires thorough and proper evaluation and diagnosis before adequate treatment can be recommended. It is best to let the specialist examine your injury and determine cause of pain.
Home remedies
Sometimes it is enough to allow your organism to rest long enough in order to heal. Cooling the painful area with ice for 10-15 minutes (just about anything that you pick from your freezer and wrap in a towel will do) can soothe pain and diminish swelling if there is any. Compression and elevation also prevent swelling. Some over-the-counter medications can be used, but doctor's advice is recommended in that case.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...