Osteopenia
Osteopenia is a medical condition which features with loss of bone density. This means that bones become thinner. Luckily the bone loss in osteopenia is minor comparing to osteoporosis. Nonetheless, patients who have been diagnosed with osteopenia have to pay attention to this condition since it eventually leads to osteoporosis. Osteopenia can be defined as introduction to osteoporosis.
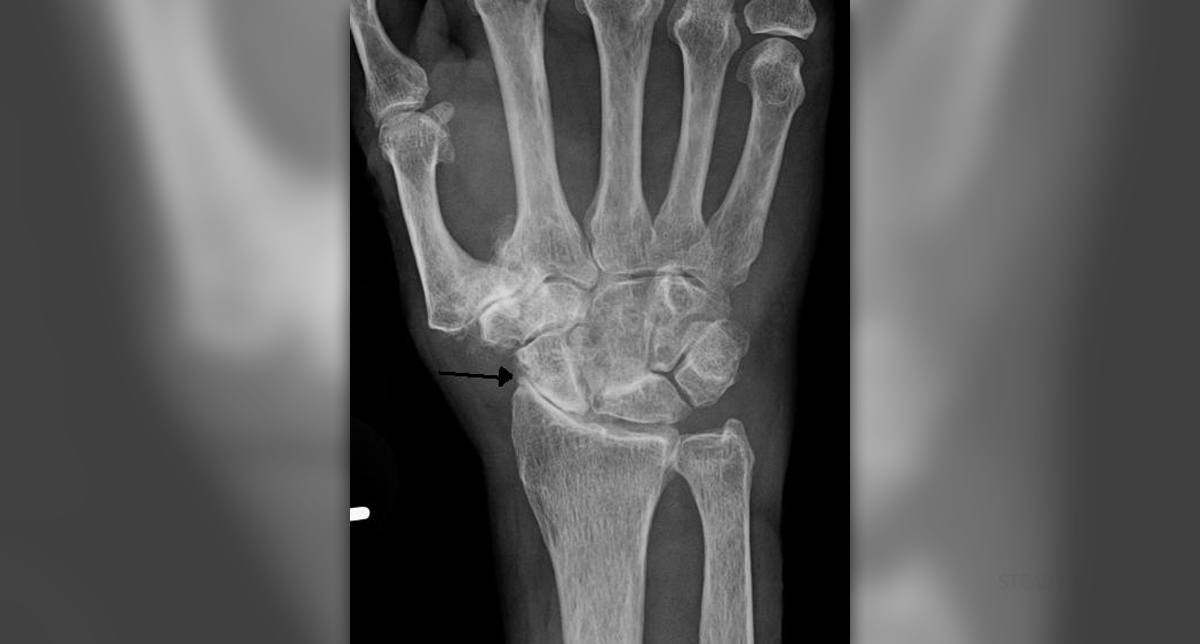
The diagnosis can be set after Dexa scans. This scan measures the bone density in hips and spine.
Osteopenia and later osteoporosis usually develop as a consequence of improper diet and insufficient physical activity or they can result from other illness or certain treatment modalities. Some believe that menopause in women may lead to osteopenia.
Still, it is evident that osteopenia most commonly results from improper life style. Making certain changes in life style can reverse the process of bone loss and help in strengthening of the entire skeleton.
Causes of Osteopenia
Human bones are constantly changing. Old bone cells die and they are replaced with the new ones. Osteoclasts are bone cells in charge with removal of old bone cells while the role of osteoblasts is to create new bone cells. The growth of bone can be achieved only with higher activity of osteoblasts. This is especially noticeable in children. In adults bones do not grow any more but the replacement of old and new bone cells continues. In 30s this process starts to reverse. This is why the strength of the bones needs to be achieved by the mid 30s. This is done by proper diet and regular physical activity.
The countries in which osteopenia occurs most include those where people tend to develop improper eating habits. Inadequate diet, together with smoking and reduced physical activity is the leading cause of this condition.
Apart from the previously mentioned certain medical conditions can induce osteopenia.
Treatment for Osteopenia
Osteopenia is reversible and absolutely treatable. The best way is to achieve the proper strength of bones in youth.
Best prevention is obtained from proper and sufficient daily intake of calcium. Apart from calcium other minerals and vitamins which are essential for bones need to be taken as well. They include magnesium, trace minerals, vitamins D3 and K2. Calcium can be obtained from many foods.
Vitamin D will help with absorption of calcium. Exposure to sun can be effective in production of vitamin D or it can be taken with certain foods. Magnesium can be also obtained from specific foods or it can be taken in a form of supplements. Vitamin K2 has been proven to be effective in maintenance of the healthy and strong bones. The body cannot produce vitamin K2 so it can be only obtained from food.
And finally, regular physical activity will additionally help in reduction of bone loss as well as in maintenance of muscle strength which will indirectly prevent fractures.
Annual spinal fractures in the United States exceed 700 000, with more than 300 000 hip fractures. After hip fracture, 25% of Americans will succumb, and another 25% will never leave the nursing institution to which they are admitted following hospitalization. The United States currently spends an estimated $19 billion on the more than 2 million annual fragility fractures and the 500 000 hospitalizations these entail.
- Yoga classes are a dramatically low-cost and less dangerous alternative to medications and the elaborate health care their absence is alleged to engender. The “side effects” of yoga include better posture, improved balance, enhanced coordination, greater range of motion, higher strength, reduced levels of anxiety, and better gait. Improved posture directly addresses spinal fractures, while all of these documented benefits of yoga reduce the risk of falling, which is the main cause of all other osteoporotic fractures. The current study examines the proposition that yoga is a safe and effective means of preventing osteoporosis-related fracture.
- Contemporary medicine accounts for bone loss or gain by genetics, nutrition, hormones, medications, and activity. The main preventive measures are based on nutrition, such as vitamin D and calcium supplementation; medications, such as bisphosphonates and serum estrogen receptor manipulation; and activities such as gym workouts, running, and sports.
- A total of 741 patients joined the study between 2005 and 2015, of whom 227 were identified as compliant with more than every-other-day yoga. Women comprised 202 of these patients. Mean age at joining the study was 68.2 years. Entry DXA scans showed that 174 (83%) of the compliant patients had osteoporosis or osteopenia.
- In all, 109 fractures were reported on prestudy radiographs and in the induction forms, and 19 in subjects postentry. As of this writing, with more than 90 000 hours of yoga practiced largely by people with osteoporosis or osteopenia, there have been no reported or X-ray detected fractures or serious injuries of any kind related to the practice of yoga in any of the 741 participants. Bone quality of the 18 patients completing the study was judged as superior to those without yoga experience.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...