Calcium is one of the essential minerals for numerous processes in human bodies. Out of all minerals, calcium is the most present in our bodies. It is involved in building of our skeleton and in charge with preservation of our bones and teeth. It takes part in contractions of the muscles and secretion of some hormones and enzymes. Calcium plays considerable role in the constriction and vasodilatation of blood vessels and clotting of the blood. Its general welfare is therefore so evident that it needs to be taken regularly in order for our bodies to function properly. Deficiency of this vital mineral can result in different states.
This mineral is present in most dairy products as well as in eggs, leafy vegetables, nuts, legumes and whole grains. Vitamin D is fundamental for absorption of the calcium. Most of the absorbed calcium is taken by bones. The rest stays in the blood.
The easiest way to spot calcium deficiency is to look at someone's nails and skin. In deficient people, nails are brittle and skin is dry. Yellowing of the teeth can also direct to calcium deficiency. Most significant are muscle cramps, twitching of the eyes, leg tensions, weakness and aches in muscles and sleeping disorders. These symptoms and signs must be taken seriously and if not treated on time may lead to serious health problems.
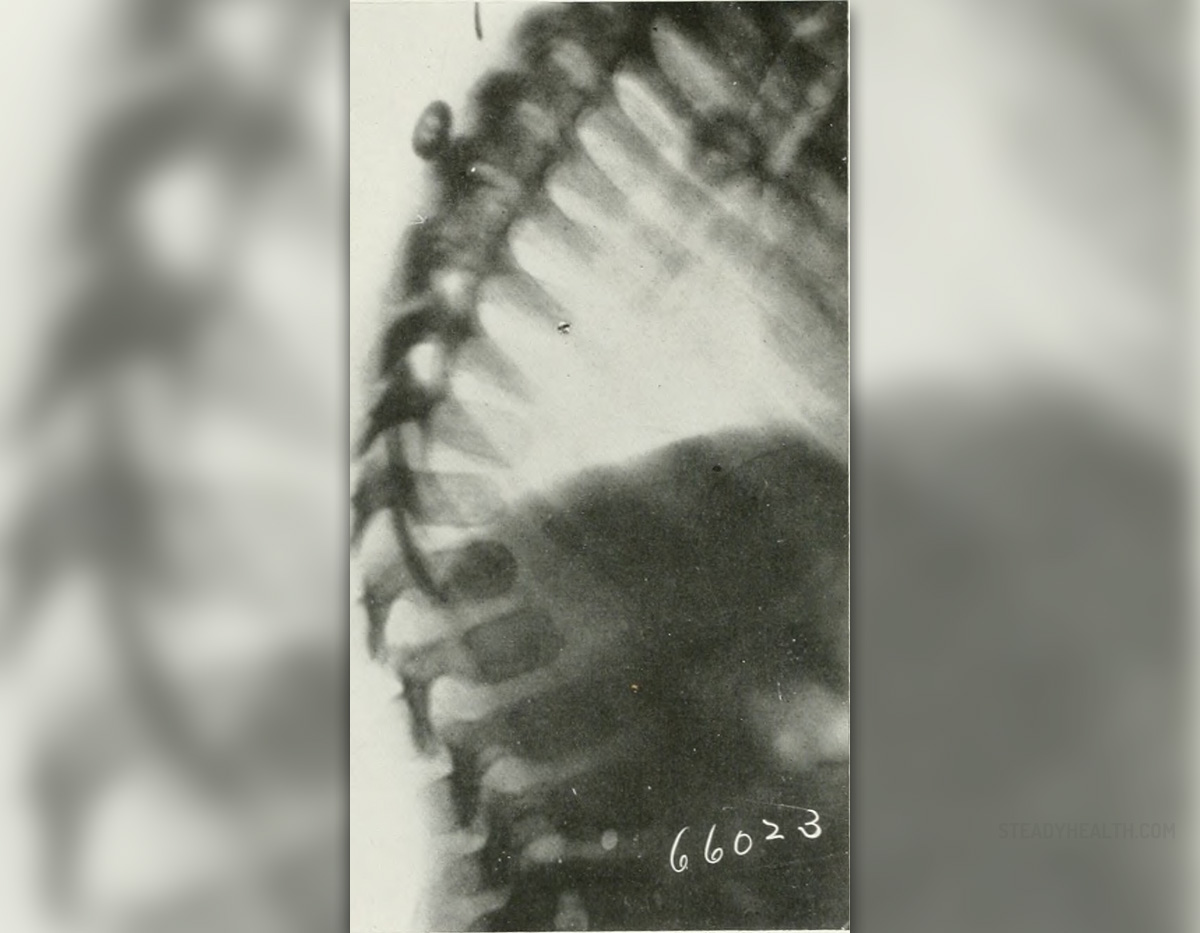
Prolonged calcium deficiency relates to abnormalities of skeleton. Bones are brittle and easily broken. The bone density is reduced hence they are thinner and not so strong. If neglected all of the previously mentioned can result in osteopenia, osteoporosis and osteomalacia. Some other conditions can rarely point to calcium deficiency. These include kidney stones, unusual menstrual cramps, hypertension or miscarriages.
As for women they absorb less and less calcium with age. Therefore they need to stick to regular daily intake. In young girls calcium deficiency leads to irregular periods, menstrual cramps, late puberty and anemia. The body also becomes more susceptible to infections. In women the greatest need of calcium is during pregnancy. Calcium is then additionally used for the formation of the baby's bones. The symptoms of calcium deficiency in women after delivery include severe bleeding and lack of milk production. Postmenopausal women are at risk to develop both osteopenia and later osteoporosis due to deficiency.
Higher amount of calcium is required in infants and adolescents. This is because they are growing and their bones are forming. In some cases if a mother is calcium deficient she gives a birth to a calcium deficient child. These children do not develop strong bones and the growth of the bones is improper. They are prone to problems with digestion and diarrhea as well.
Adequate calcium intake during life time therefore not only helps children to develop and grow properly, but it also prevents for possible later conditions such as osteoporosis.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...