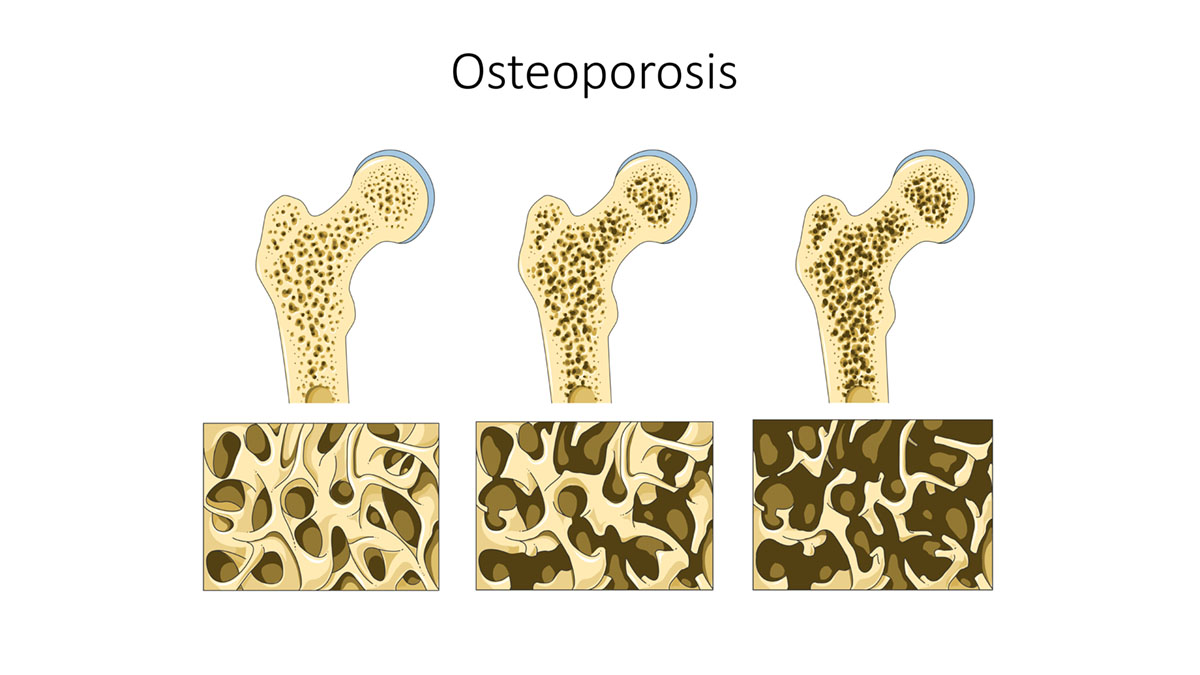
Osteoporosis is a bone disease with decreased bone mineral density (BMD) and increased risk of bone fracture. It usually affects menopausal women and older people, over 60. Bones are constantly changing in our body. Osteoblasts are the bone cells that produce new bone and osteoclasts are absorbing the bone. After 60, or without enough estrogen (in menopause) osteoclasts are much more active and that increase bone thinning, sometimes causing osteoporosis.
The treatment for the illness is the group of medications called bisphosphonates, which block the osteoclasts and affects the process of osteoporosis. The most commonly use bisphosphonates are Alendronate sodium (Fosamax) and pamidronate disodium (Aredia).
Fosamax tablets must be taken exactly as your doctor prescribed them. Usually, they are taken without food or any other medication, at least 30 minute before breakfast, with a full glass of clear water. It is recommended to stay up or sit for that time so don’t lie down after you had the tablets. Try to swallow the tablet, for sucking or chewing might cause mouth sores. Calcium and vitamin D supplements are advisable but do consult your doctor before you start taking them.
Alcohol and smoking should not be used, try to avoid them.
Bisphosphonates are long-term medication and side effects are still reported. Fosamax is known to cause appetite loss, swallowing problems, abdominal pain and distention, constipation and esophageal ulcer.
Some of the Fosamax patients have severe complications. Falling from a standing or sitting height might cause patients treated with Fosamax to experience femoral fractures. More than 30% of all of the patients with subtrochantric and femoral shaft fractures were treated with bisphosphonates. Possible explanation is that the medications affect the collagen in the bone weakening it and making these patients more prone to fractures.
Solution for minimizing this side effect is a "drug holiday". The doctor would stop the medication after 5 years, and patients would be treated with calcium and vitamin D. If the bone loss starts again, doctor would prescribe another lower dose of the drug. Some of the patients suffer from serious muscle and bone pain which is stopped by canceling Fosamax.
Fosamax is reported to provoke heart rhythm problems, such as atrial fibrillation. The FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) has stated (based on a 19000 patients study) that this medication is not connected with the risk of atrial fibrillation. Rare but severe side effect in Fosamax patients is esophageal cancer.
Dentists reported osteonecrosis of the jaw bone in some of the patients using Fosamax. Possible solution might be to check your teeth first and then start with bisphosphonate treatment.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...