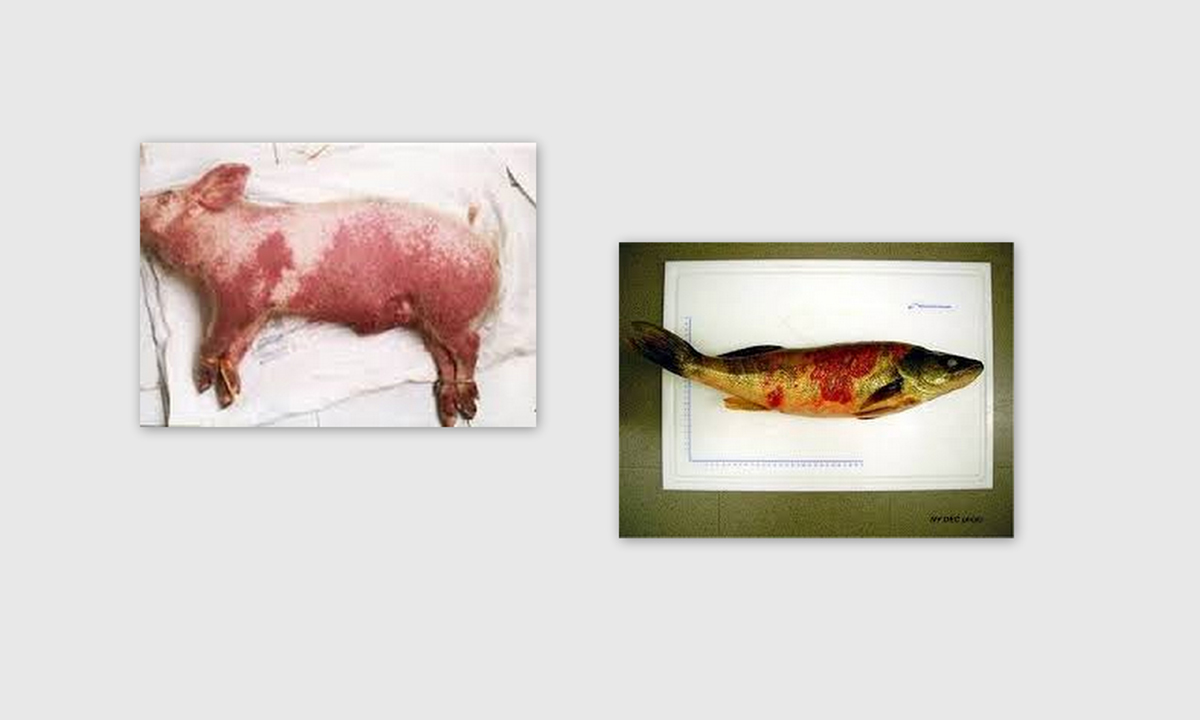
Septicemia is the name for the blood infection, but it is also well-known under the names septicemia, bacteremia and blood poisoning. This condition is caused by the same bacteria that causes the meningitis. Since it is a very serious condition, it must be treated immediately, otherwise it can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of septicemia
The symptoms of septicemia are easily noticed. Since it is the blood infection, the infection spreads throughout the whole organism because it is carried by blood. In the early phases, septicemia has the sighs that resemble those symptoms of the flu, such as fever, chills, loss of appetite and tiredness, as well as the increased heart rate. The symptoms of septicemia are also hypothermia, which is the medical term for a significant drop in the body’s temperature, and hypotension or low blood pressure. Furthermore, the person with septicemia hardly has urination.
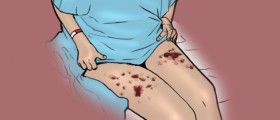
The most common symptoms of this condition are acute inflammation that occurs in the whole body, high fever, shivering, sweating and flushing, as well as pains, low or high body temperature and increased or decreased levels of leukocytes or white blood cells. Other symptoms include high heart rate, high respiratory rate, nausea and vomiting. Those people with septicemia may also experience blood clotting, which causes the appearance of red spots on the skin. To establish this condition, urine and blood test are done, although many doctors practice lumbar puncture in order to detect it. If it is not treated promptly, septicemia may lead to a septic shock, which is fatal in the majority of cases. The people in whom septicemia is diagnosed in the early stages, as well as those with the strong immune system, have higher chances to be cured.
Treatment of septicemia
The patient with septicemia diagnosis must be hospitalized and the treatment then depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. First of all, the blood pressure must be kept normal. Sometimes, the oxygen therapy is needed, while in some cases the infection source can be drained or surgically removed. Before the exact cause is detected, many antibiotics are taken, but when the cause is established, a specific antibiotic is given to the patient. In order to prevent septicemia there are specific vaccines that are administered to children. It is advisable that even those people who are close to the patient with septicemia receive the prescribed preventive antibiotics for immunization.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...