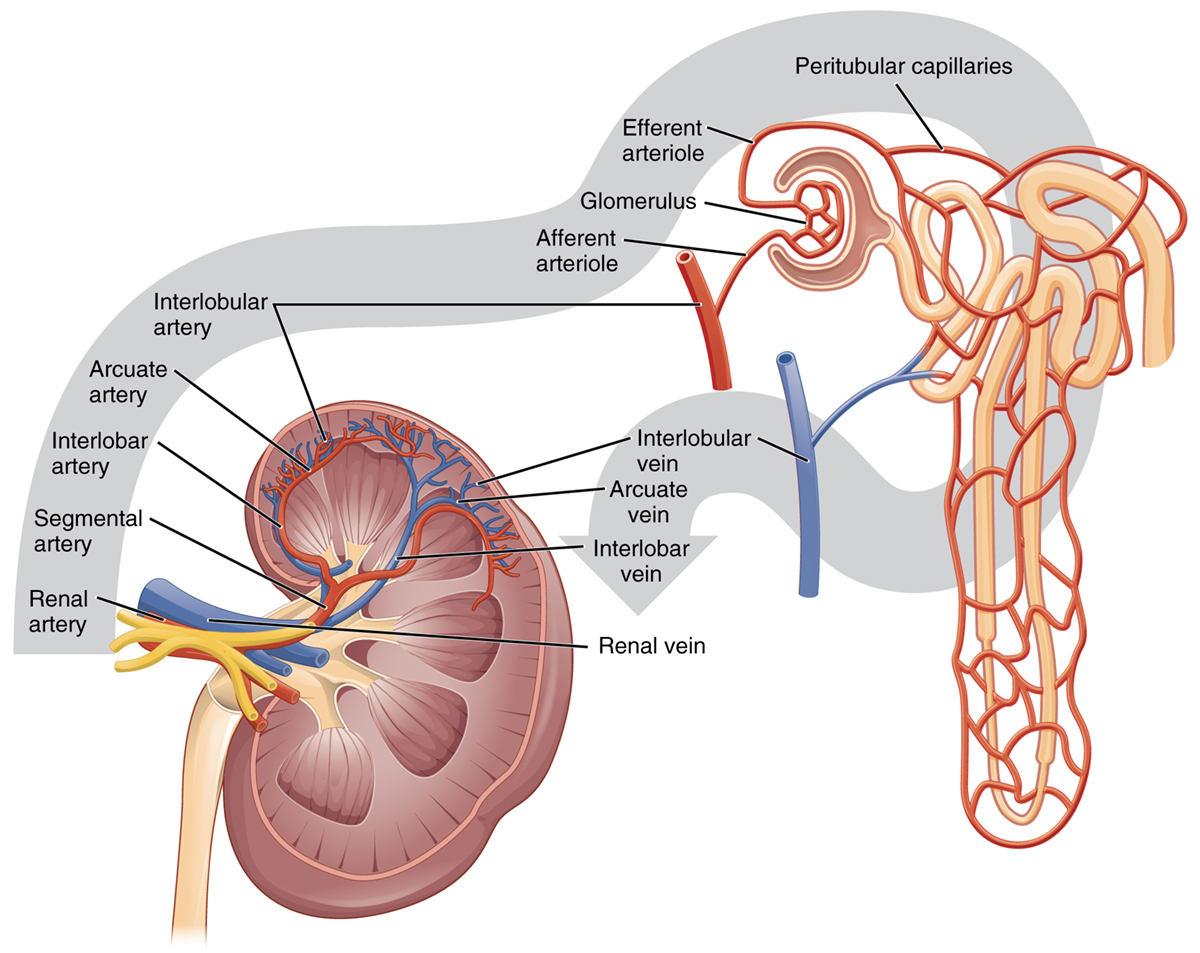
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is the medical term for the kidney infection. This type of urinary tract infections first affects bladder or urethra and then progresses and affects the kidneys and it must be treated immediately in order to avoid some serious damage of the kidneys or some serious infections that may be even fatal.
Causes and Symptoms of Pyelonephritis
This type of infection occurs when bacteria penetrate through the urethra into the urinary tract. There are cases when bacteria from some other infection in the body spread to the kidneys through the blood while only few cases when pyelonephritis occurred as the result of the kidney surgery have been reported.
There are many warning signs and symptoms of the kidney infections, and the most frequent are pain in abdomen or pain in the back, side or groin area. Furthermore, frequent urination, constant urges to urinate and pain while urinating are also some of the signs of this disease.
Hematuria may also appear, and it is the medical term for the condition when pus or blood appears in the urine. Some persons who suffer from pyelonephritis complain of high fever as well. It is very important to visit the doctor if some of these signs appears. The doctors usually prescribe antibiotics to treat this disease and the patient must be hospitalized.
Complications of Pyelonephritis
Kidney infection can be mild or acute and severe or chronic. The severe pyelonephritis can cause many serious complications such as permanent kidney damage, septicemia, and complication during pregnancy. Pyelonephritis is one of the causes for the occurrence of the permanent kidney damage that, further may lead to the chronic kidney failure. This is only one of the reasons why this disease must be treated promptly.
Acute pyelonephritis can be divided into uncomplicated and complicated. Complicated pyelonephritis includes pregnant patients, patients with uncontrolled diabetes, kidney transplants, urinary anatomical abnormalities, acute or chronic kidney failure, as well as immunocompromised patients and those with hospital-acquired bacterial infections. It is important to make a distinction between complicated and uncomplicated pyelonephritis, as patient management and disposition depend on it.
- Acute pyelonephritis can have several complications such as renal or perinephric abscess formation, sepsis, renal vein thrombosis, papillary necrosis, or acute renal failure, with one of the more serious complications being emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN).
- Emphysematous pyelonephritis is a necrotizing infection of the kidney usually caused by E. coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae and is a severe complication of acute pyelonephritis. EPN is usually seen in the setting of diabetes and occurs more frequently in women. The diagnosis can be made with ultrasound, but CT is typically necessary.
- Overall the mortality rate is estimated to be approximately 38% with better outcomes associated with patients who receive both medical and surgical management versus medical management alone.
- Complicated pyelonephritis includes pregnant patients, patients with uncontrolled diabetes, transplant patients, those with urinary anatomical abnormalities, acute or chronic kidney failure, as well as immunocompromised patients.
- Old age (older than 65 years), male gender, impaired renal function, or presence of disseminated intravascular coagulation are associated with increased mortality.
Furthermore, septicemia may also happen, and it is a medical term for the poisoning of the blood. The main role of the kidneys is to filter waste from the blood and after filtration to return the blood. In the case when the kidney is infected, bacteria can enter the blood and spread though the bloodstream.
In the case when pyelonephritis appears in a woman is pregnant, one of the consequences may be that the newborn baby has very low weight or that the baby is prematurely born. Other complications of pyelonephritis includes perinephric abscess and acute papillary necrosis. In some cases renal abscess may also occur. All these above-mentioned complication usually occur in patients that suffer from diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure renal transplant AIDS and sickle cell disease.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...