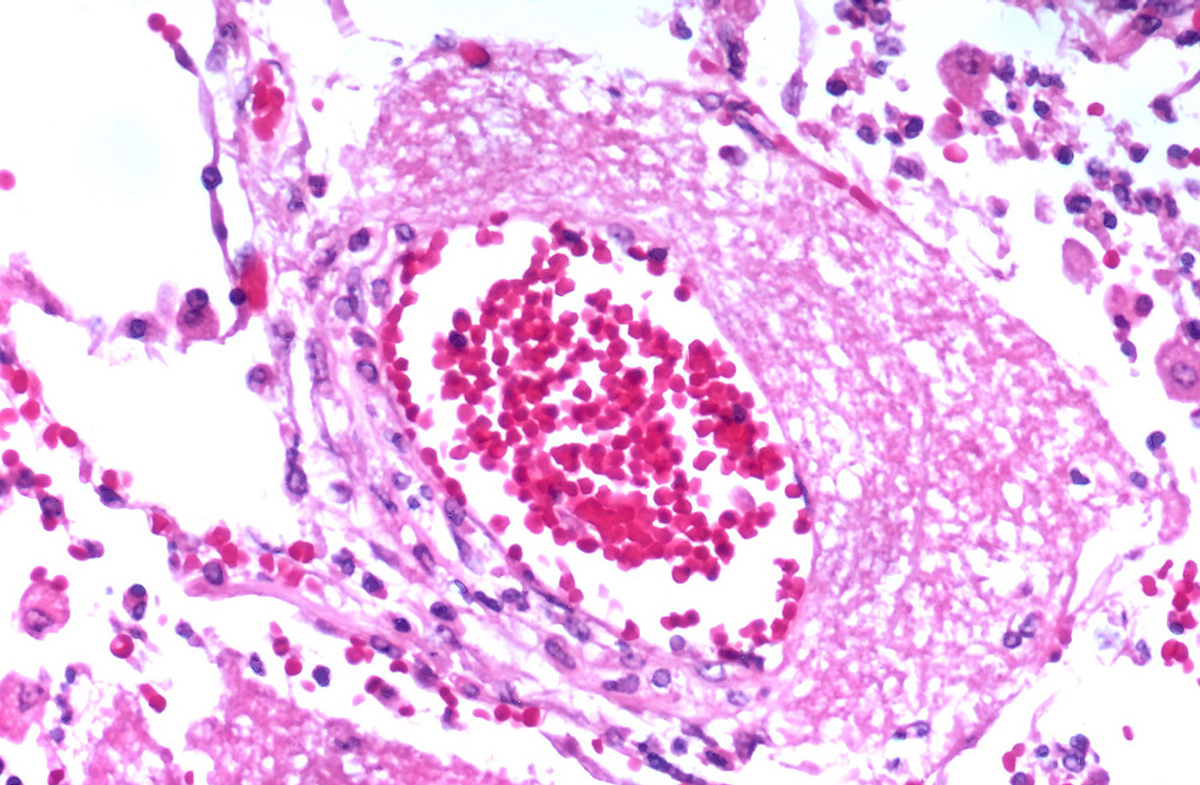
Blood infection in children is, similarly to blood infection in adults, a serious and potentially life-threatening medical condition. Blood infection is also known as septicemia and it develops as a consequence of whole body inflammatory state due to a known or suspected infection. The infection spreads from some localized body part to the blood stream. The very presence of infective agents or their toxins in the blood stream induce severe body reaction and subsequent damage. If left untreated blood infection in children can cause damage to many organs such as lungs and kidneys and it may lead to lethal outcome.
Causes and Symptoms of Blood Infection in Children
Blood infection occurs more in predisposed children i.e. those whose immune system is not strong enough. The infective agents may enter the body through cuts on the skin or spread from already infected body organs and move to other organs such as the lungs, liver, kidneys or intestines. This medical condition most commonly affects children suffering from sickle cell anemia, AIDS infection, cancer and pneumonia. In children who are on prolonged corticosteroid therapy the immune system is suppressed and not able to fight infection successfully. These children are also more susceptible to blood infection.
In most cases blood infection features with high fever and chills, rapid heart rate and rapid breathing and low blood pressure. Furthermore, a child may feel nausea and vomit. Urine output significantly decreases, the child may lose consciousness and there are problems with coagulation.
Treatment for Blood Infections in Children
Blood infection or septicemia can be diagnosed if a doctor takes samples of blood and examines them in laboratory. This way the presence of infective agents or their toxins can be confirmed. Further investigation may include sputum or urine so that the primary source of infection can be identified as well. The doctor may perform several more tests and examinations and complete blood test and chest X-ray are only two.
The treatment for blood infection includes high doses of antibiotics. Only this way infective agents can be successfully eradicated and damage to organs and organ system successfully prevented. It is essential to start treatment immediately even prior getting results form the laboratory. Patients are initially administered broad-spectrum antibiotics intravenously and after results are obtained the doctor may change an antibiotic with more suitable one. Some patients may require oxygen support and in those with low blood pressure saline solutions are administered. The entire treatment takes place in a hospital and during the treatment and until a child is stabilized there is need for permanent monitoring of all the vital functions which can be severely affected during blood infection.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...