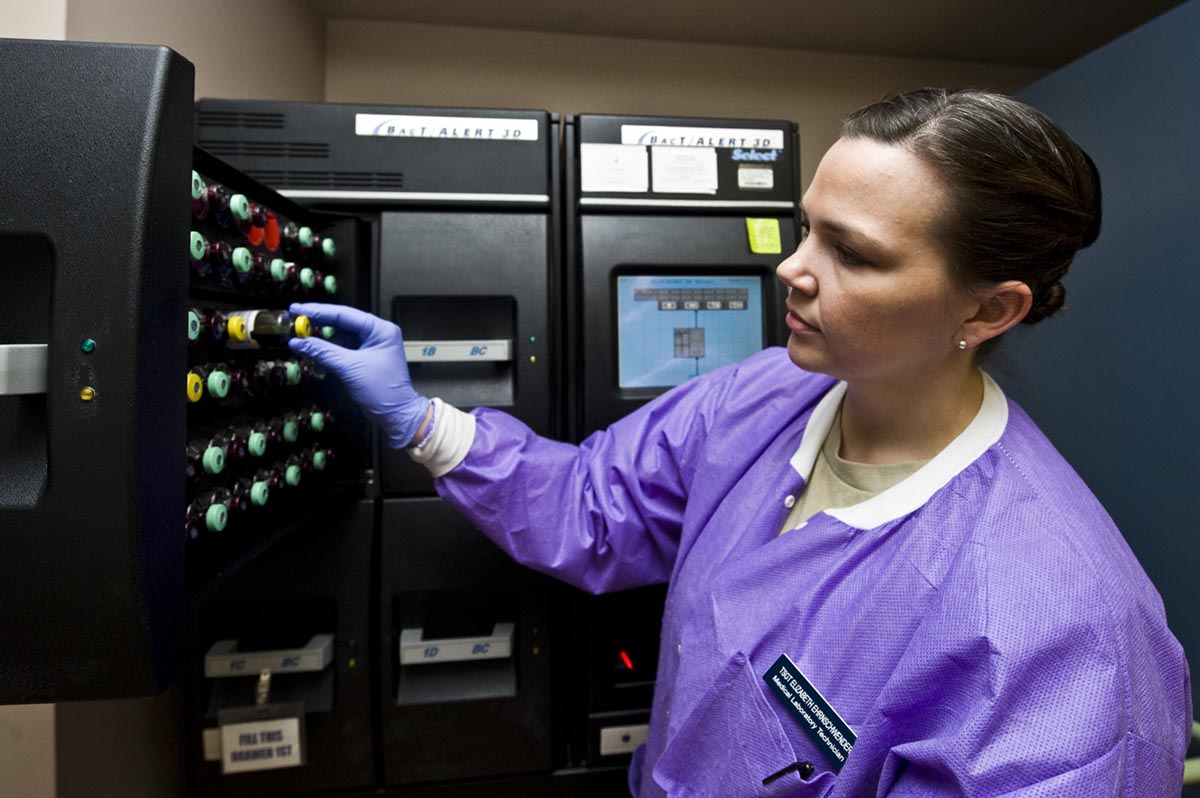

Sepsis is a severe medical condition described by a whole-body inflammatory response and the presence of an infection. This inflammatory response may be triggered by the immune system reacting to microbes in the blood, urine, lungs, skin and other tissues. Blood poisoning is the most commonly used nonspecific term to describe this medical condition. However, this is not a medical term and it doesn’t show up in medical dictionaries and publications.
Understanding sepsis
Sepsis is an extremely dangerous and the life threatening medical condition. It develops in presence of a known or suspected infection caused by bacteria and commonly many other kinds of irritants. Sepsis, or blood poisoning, is distinguished by occurrence of acute inflammation present all over the entire body, normally associated with fever and increased number of white blood cells, also known as leukocytosis. Patient’s body temperature is either high, more than 100.4F or 38C, while patient’s leukocyte readings show more than 12000 cells/.
In some cases, blood cell count may be low and bodily temperature is lower than the average, accompanied with vomiting. Temperature is lower than 96.8F or 36C, and the blood cell count is less than 4000 cells/µL or >10% bands (immature type of white blood cells). Patient’s heart rate is elevated to more than 90 beats at rest. This condition is known as tachycardia. Patient’s respiratory rate counts more than 20 breaths per minute or partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO2) is lower than 32 mm Hg.
Patients that meet those criteria are proclaimed septic. Terms that may also refer to sepsis are bacteremia, septicemia and, already mentioned, blood poisoning. Bacteremia, however, takes place with the presence of bacteria in the bloodstream. It can come about without any of the criteria we mentioned in this article, so it shouldn’t be confused with sepsis.
Causes of sepsis
Great numbers of sepsis infections are being caused by bacterial infections, fungal infections and just a few due to other causes of infections. The infectious agents affect all of the organs or implanted devices (like skin, lung, gastrointestinal tract, surgical sites, intravenous catheter and so on). Toxins and other infectious agents are being spread further to the bloodstream causing the inflammation of every other organ in the system. When the body reacts to the infection the symptoms of the sepsis take place.
The most common bacterial causes of sepsis are gram-negative bacilli like E. coli, P. aeruginosa, E. corrodens, and other species like S. aureus, Streptococcus species and Enterococcus. Candida is the most common cause from the fungi family.
Patient with sepsis can be contagious and it is extremely important to take persuasions such as hand washing and use of sterile gloves, masks and clothing coverage.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...