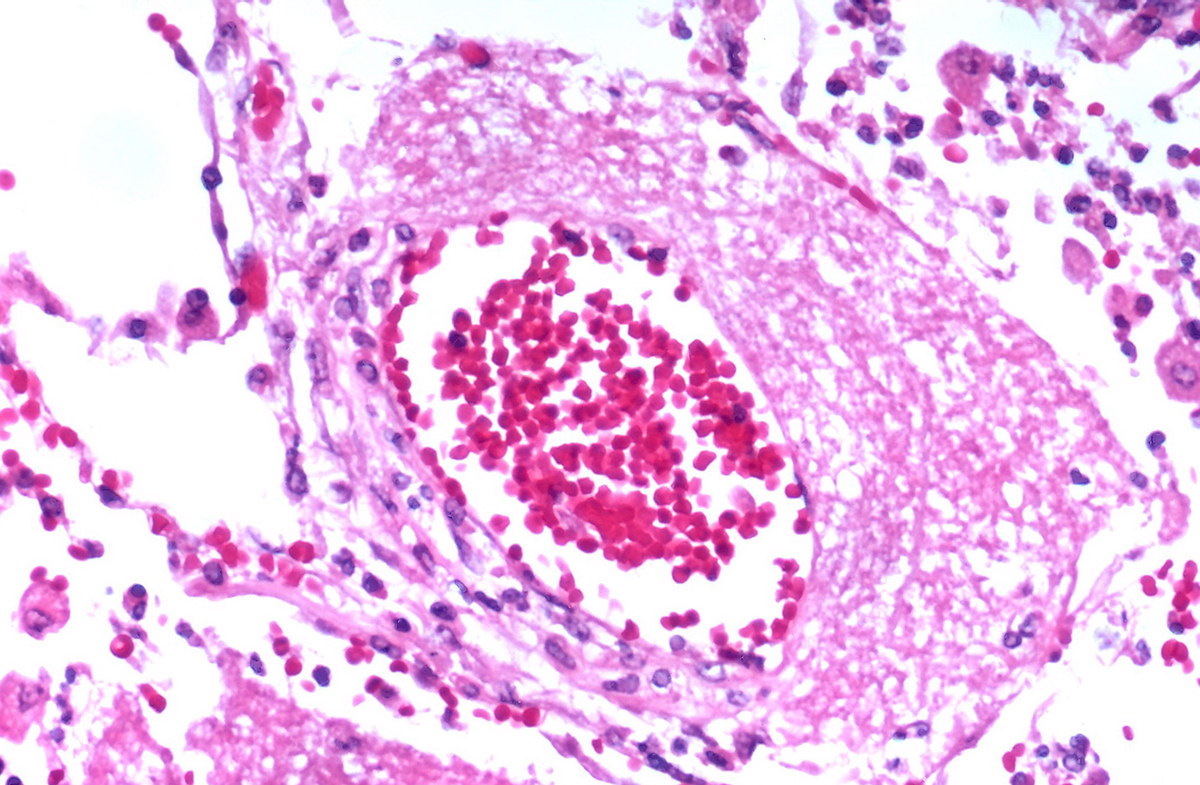
Blood infection is a disease that develops when bacterial infection spreads to the bloodstream. Medical term for blood infection is sepsis or septicemia. It can lead to a septic shock, which is a highly dangerous condition. Normally, the immune system can deal with small amount of bacteria in the blood. But, when the immune system is weakened, number of bacteria rapidly increases leading to blood infection.
Blood Infection Causes
Most commonly, blood infection is caused by bacteria but other types of pathogens like viruses and fungi can cause the disease too. Inappropriate personal hygiene and contaminated living environment can cause infection in the blood. Blood infection can develop after invasive medical procedures due to inadequately sterilized surgical tools. The condition can also result from infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, cellulites and meningitis that spread and lead to sepsis. Ruptured appendix too can lead to blood infection. People treated with immunosuppressive medications are at the high risk of blood infection as well as those with large burns and serious injuries. People with weakened immune system such as cancer, AIDS and diabetes patients are susceptible to the infection too. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation cause weakening of the immune system thereby cancer patients are prone to blood infection. Long term use of steroids also impairs the immune system and can be responsible for blood infection in some people. Infants easily develop blood infection because of their undeveloped immune system. In children below one year of age, sepsis can result from some minor infection that is not adequately treated or identified on time. Elderly people are also at high risk of blood infection because of their lower immunity that naturally comes with age. Finally, people who have had spleen removal are at the high risk of infection in the blood.
Blood Infection SymptomsSymptoms of blood infection can vary from a patient to patient depending on the severity and the primary cause of sepsis. Blood infection is most commonly followed by high fever, chills and shivering. Decrease in blood pressure, rapid heart beat as well as rapid breathing often accompanies sepsis too. Other symptoms associated with infection in the blood are: skin rash, swelling and pain in the joints, confusion, disorientation, agitation, dizziness and decreased urination.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blood InfectionThe presence of blood infection can be confirmed with the use of tests such as blood culture, urine culture, spinal fluid analysis, CT scan, X-rays and others. A patient with blood infection requires prompt medical treatment. The treatment is usually given in an intensive care unit where the patient receives intravenous antibiotic therapy. Chances of survival increase if the treatment begins without delay.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...