
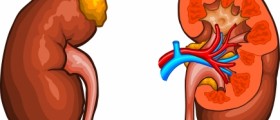
About kidneys
Kidneys are paired organs located at each side of the lowerabdomen, which produce urine stored in the bladder and then passed outthrough the urethra. Sometimes the kidneys might become infected, which ismedically referred to as pyelonephritis, and although people of all ages can beaffected, kidney infections are most typical of women. Sometimes the bacteria from the bladder can reach the kidneycausing the infection, while other causes of pyelonephritisinclude kidney stones or blocked urethras. Under certain conditions, bacteriafrom the bloodstream may end up in kidneys.
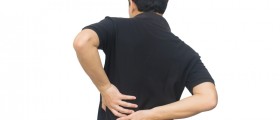
Although a kidney infectionsometimes just gives the person a general feeling of being unwell, symptomsassociated with this condition include nausea or vomiting, diarrhea, a highbodily temperature or fever, painful urination, pain in the lower back orabdomen, dark, cloudy or even bloody urine, and a frequent need for urination,although there is not much urine to pass. However, the person does notnecessarily have to experience all of these symptoms.
Conditions
There is a risk of developing chronic condition if theinfections are repeated, and this is usually the case when another kidney problemis involved (e.g. large kidney stones). Doctors can usually tell by the person’s symptoms if theyhave the infection or not, while sometimes running urine or a blood test is necessary. If the doctor suspects that another kidney condition is causing theinfection, then the person undergoes an x-ray, MRI or CT scan, and this isespecially the case with men and children, since they are less prone to kidneyinfections. Antibiotics are a common treatment for most kidneyinfections, but if the person is in pain or is running a temperature, doctors mayalso advise the use of painkillers. During the kidney infection, there is a risk of dehydrationso the recommended daily intake of water is 2 litres, provided thatthe person is not affected by another condition preventing them to drink so muchfluid. A person might be admitted to hospital if they have severesymptoms, if facing dehydration or if the infection does not clear up afterthe course of antibiotics, and an intravenous antibiotictreatment that has a more rapid effect is necessary then.
Kidney infections usually pass without any complications, but sometimes they cause the formation of an abscess (a collection ofpus), so surgery might be required to get rid of the accumulated pus. If left untreated, kidney infection poses a risk ofsepticemia (blood poisoning) as a result of the bacteria ending up in thebloodstream. People who continue to get kidney infections are at risk ofscar formation and other permanent harm to the kidneys. The doctor will thendecide about the best way to manage the damage done to kidneys.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...