Sepsis is a rather serious and potentially lethal condition caused by the presence of bacterium or bacterial toxins in the blood. The patient who develops sepsis has been suffering from infection of certain organ or organ system and the culprits have entered the blood stream leading to severe reaction of immune system. In sepsis normal functioning of organs is affected and even a shock might occur.
There are certain groups which are prone to sepsis more than other patients. These includes very young people and elderly patients. Immunocompromised people tend to develop sepsis more than others. Hospitalized people are prone to sepsis more as well as those who are intubated or due to health condition have to carry urinal catheters. The condition must be diagnosed at once and aggressive treatment with intravenous antibiotics and fluids must begin as soon as possible.
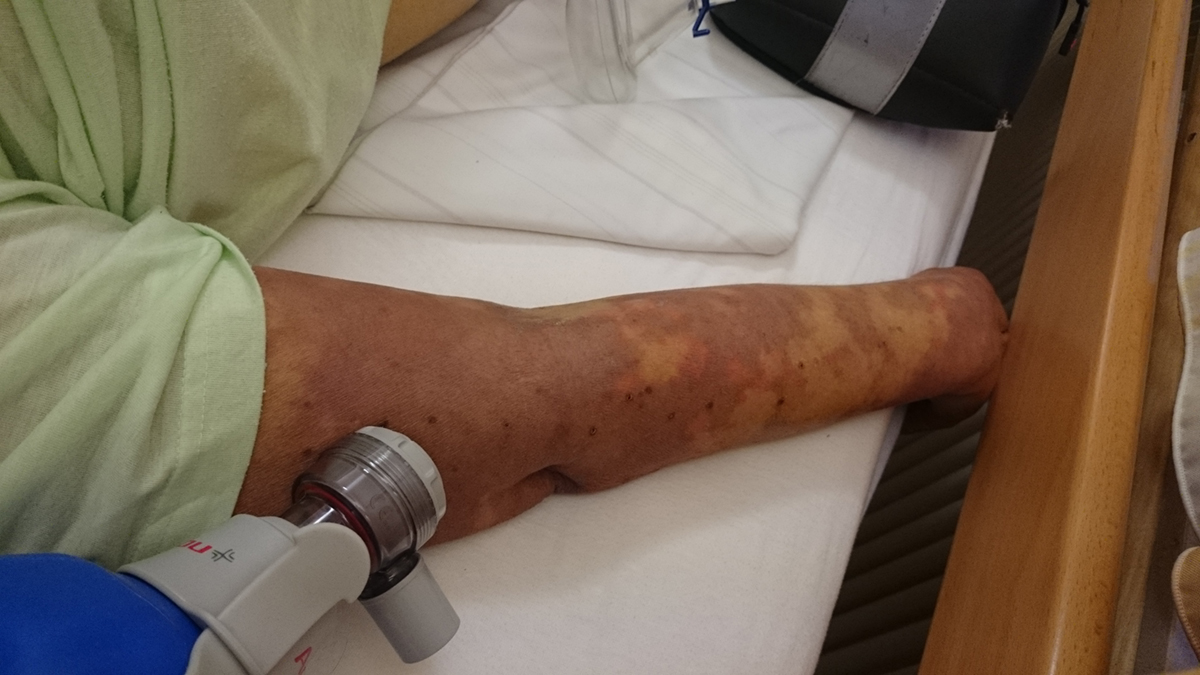
The symptoms of this life-threatening state include high body temperature (above 101.3 F). The heart beats faster than usual reaching 90 beats per minute. Breathing is accelerated as well. All of these symptoms are patognomonic in all the patients who have previously been hospitalized but have not shown any signs of progression of the initial infection.
In case of that condition is not recognized on time the sepsis progrades and additional symptoms develops. They include the skin changes, reduction of number of platelets, retention of urine and abnormalities in mental status of the patient. The heart rate goes even higher than in the beginning of the disease and the patient expresses severe problems with breathing.
In case the sepsis shock develops it presents the initial symptoms and signs of the disease together with abnormally low blood pressure.
In hospital environment doctors monitor patients who are at higher risk and may observe the early signs of sepsis. Still all those who are not hospitalized and are under infection of any kind it is essential to visit their doctors as soon as possible if any of the previously mentioned symptoms occur.People at risk are treated in hospitals even in case of minor infections as the possibility of sepsis in these patients is rather high.
Nonetheless even those who are at home and show the initial signs of sepsis after the hospitalization the condition can be brought under control. During the transport to the hospital they are given oxygen and monitored for any change in vital signs. IV line is opened for easier drug application. After the admission into the hospital the patients are further analyzed and treated according to prescribed regimes and standards.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...