
Type 2 Diabetes - Introduction
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease and features with high levels of sugar in the blood. Unlike the type 1 diabetes in which there is no insulin at all in type 2 diabetes patients may have sufficient amount of the insulin in the blood but they simply cannot use the available glucose due to the presence of insulin resistance.
The goal of the therapy in type 2 diabetes is to eliminate all the symptoms and signs of the disease and normalize levels of sugar in the blood. The treatment initially includes dietary changes and physical activity and if the disease progresses the patients are prescribed certain medications. It is also essential for all people suffering from diabetes to regularly control the level of sugar in the blood. Blood sugar testing is easily performed and the results are interpreted and significantly influence the further treatment of the disease.
Treatment for Type 2 DiabetesDietary ChangesBy choosing proper food patients can bring increased sugar levels under control. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider and a registered dietitian who will decide and even make the best suitable diet for a person suffering from type 2 diabetes. Dietary plan must meet patient's eating habits and preferences and be adjusted to work and additional activities such as sport and similar.Physical ActivityRegular physical activity is not only recommended to people suffering from type 2 diabetes. It is essential for all people in case they want to stay healthy. In people who have type 2 diabetes regular physical activity increased utilization of glucose and reduces its levels in the blood. It is also good since many people suffering from type 2 diabetes are obese and regular physical activity may help them lose weight.MedicationsIn case that dietary changes and physical activity do not help the patient to bring the increased level of glucose under control the doctor opts for medications.
There are several groups of medications prescribed to patients with type 2 diabetes. They include oral sulfonylureas, biguanides, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, thiazolidinediones and meglitinides. The doctor chooses the most suitable medication and even though patients are prescribed medications all them must stick to their dietary regimes and continue with regular physical activity.
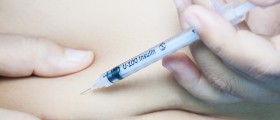
Unfortunately, in some patients oral medications cannot control the level of glucose in the blood and they eventually require insulin. Insulin is also prescribed to patients who cannot tolerate oral medications. Insulin is injected subcutaneously and the patients must follow doctor's advice and never exceed the prescribed dose since this may induce certain complications.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...