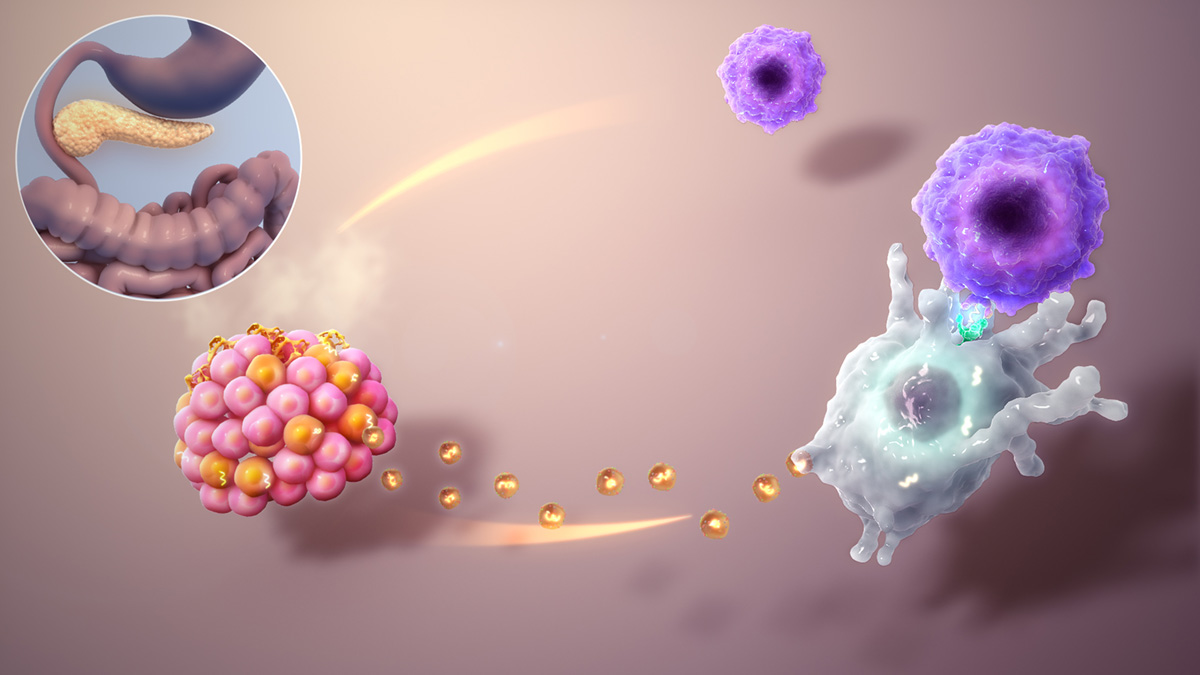
What is Type 1 Diabetes?Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition caused by lack of the insulin production. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that controls blood sugar levels. Without enough insulin, glucose instead of going into the cells builds up in the bloodstream. Because of this the body is unable to produce energy which leads to increased hunger. High levels of glucose in the blood cause frequent urination that leads to increased thirst. Other symptoms of type 1 diabetes are weight loss, tiredness and blurred vision. Type 1 diabetes most commonly occurs due to autoimmune disease that affects the pancreas gland. The condition must be treated since it may cause diabetic ketoacidosis which can lead to coma and even result in fatal outcome.
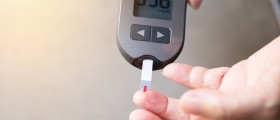
How is Type 1 Diabetes Treated?Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong treatment to maintain blood sugar level in optimal range. Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin replacement therapy. Insulin can be taken either by insulin injection or insulin pump. Patients must stay physically active and eat healthy diet with controlled amount of carbohydrates. Glucose meters must be used to regularly monitor blood glucose levels. Continuous glucose monitoring is the newest way of monitoring blood sugar levels that may alert a patient to the presence of dangerous levels of blood sugar. The device is attached to the body using a needle under the skin that performs checkups every couple of minutes. However, continuous glucose monitoring is not as accurate as standard blood sugar monitoring hence it can be used only as additional measure.
Nowadays, insulin that is most commonly used is a biosynthetic product. In the past, insulin that was used was obtained from cattle, pig and even fish. Today, insulin is made with the help of genetic recombination techniques. There are different types of insulin that are classified depending on onset of action time and how long it lasts. They include: rapid-acting insulin (insulin lispro, insulin aspart and insulin glulisisne), short-acting insulin (insulin regular), intermediate-acting (insulin NPH) and long acting insulin (insuline glargine and insulin detemir).
Pancreas TransplantationIn severe cases of type 1 diabetes, treatment may involve a pancreas transplant to restore adequate regulation of glucose. However, the side effects of pancreas transplant can be dangerous therefore this treatment is used only for patients with severe complications of diabetes. A pancreas transplant is frequently done along with or after a kidney transplant.
Islet Cell TransplantationIslet cell transplantation is used experimentally to treat type 1 diabetes. The procedure is less invasive comparing to pancreas transplant. Islet cells can be injected into the liver of a patient in order to start producing insulin. However, the body of a patient may recognize these cells as foreign body and the immune system will attack the cells. To prevent this, patient’s own stem cells should be used if possible or those of identical twin or a patient must receive immunosuppressive medications.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...