What Must People Know about Diabetes?
Insulin is a hormone normally produced by the pancreas and it plays a significant role in metabolism of sugar. Insulin maintains optimal level of sugar in our blood. There are several causes of diabetes. Namely, there is either too little insulin or there is a resistance to insulin. In some cases even a combination of the two is possible.
Patients suffering from diabetes have high level of sugar because the pancreas does not produce sufficient amount of insulin, their muscle, fat and liver cells simply do not respond to insulin normally or there is a combination of the previously mentioned.
There are three major types of diabetes, diabetes type 1, diabetes type 2 and gestational diabetes. Diabetes type 1 usually occurs in childhood and it features with little or no insulin in the body. Patients suffering from this type of diabetes require injections of insulin on daily bases. In type 2 diabetes the problem occurs in adulthood and in such patients the pancreas does not synthesize sufficient amount of insulin and the body does not respond well to insulin. This type of diabetes is commonly associated with obesity and failure to exercise. And finally, gestational diabetes affects pregnant women who have not had any problems with blood sugar before.
Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes
Elevated level of glucose in the blood leads to several problems such as blurry vision, excessive thirst, excessive hunger, fatigue, frequent urination and rapid weight loss. Still, people suffering from diabetes type 2 may be asymptomatic and the condition can be diagnosed during routine blood tests.
Type 1 diabetes typically leads to fatigue, increased thirst and urination, increased hunger and weight loss, nausea and vomiting. Type 2 diabetes features with blurred vision, fatigue, increased appetite and thirst and increased urination.
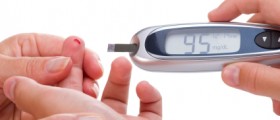
Diagnosis and Treatment for Diabetes
Blood test points to elevation of blood sugar. Furthermore, a urine analysis may point out the presence of ketones that are products of the fat breakdown. In order to definitely set the diagnosis doctors commonly perform several tests including measuring fasting blood glucose level, hemoglobin A1c test, oral glucose tolerance test and random (non-fasting) measuring of blood glucose level.
Treatment for diabetes depends on the type of diabetes. The goal of immediate treatment is to treat diabetic ketoacidosis and bring the elevated blood sugar levels under control. Long-term goals are to prolong patient's life, reduce symptoms and prevent diabetes-related complications.
Depending on the type of diabetes patients are prescribed either with oral anti-diabetic medications or insulin. Such patients must strictly pay attention to what they eat and they also need to engage in regular physical activity. Furthermore, they require regular blood pressure and cholesterol control, education, foot care and timely diagnosis of potential complications.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...