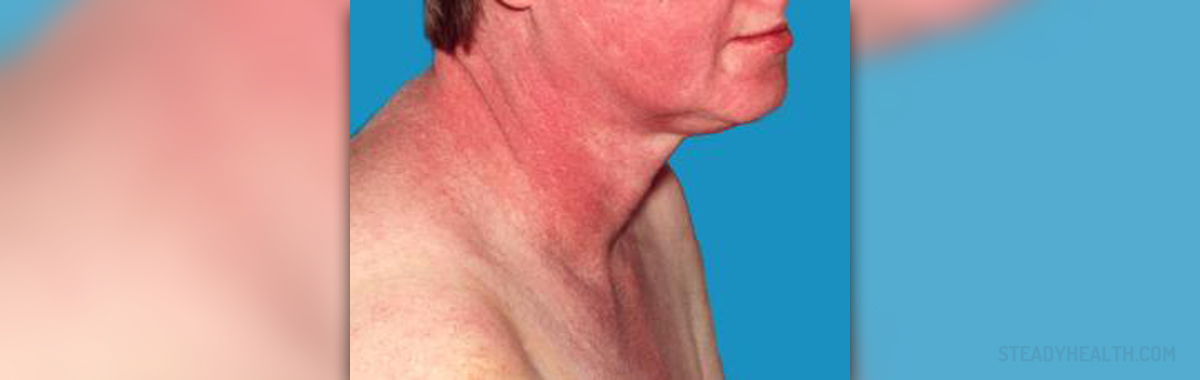
Dermatomyositis is a chronic inflammatory condition which commonly features with muscle weakness and a characteristic skin rash, symptoms that typically appear gradually over a period of time, although the onset can also be sidden in some patients. The symptoms and signs of dermatomyositis most often develop gradually over weeks or even months. Dermatomyositis may affect people of all ages. Still, this medical condition is most frequently seen in people in their late 40s to early 60s. It is also common for children between the ages of 5 and 15. This condition predominantly affects women.
Dermatomyositis: What Are its Causes?
This disease belongs to a group of so called myopathies, which means that it is a disease in which muscle fibers do not function as they would in an unaffected person. The exact cause of most myopathies is still unknown. Some assume that the inflammation may be associated with infections (bacterial, parasitic or viral infections). Others believe in genetic susceptibility to dermatomyositis. This condition has many characteristics of autoimmune diseases, as well. Namely, the immune system produces autoantibodies which destroy the body's own cells. In this medical condition the process of inflammation particularly affects the small blood vessels in muscular tissues. In a majority of patients, there are circulating antibodies which can be easily detected using lab tests.
Dermatomyositis: What Are the Symptoms?
The inflammation seen in patients with dermatomyositis typically affects the skin and the muscles. The skin is violet-colored or it may be covered in a dusky red skin rash. The rash predominantly develops on the face and eyelids, around the nails, on the patient's knuckles, elbows, knees, chest and back. The rash can be patchy and in some patients there are bluish-purple discolorations.
The affected muscles become weak and the weakness is progressive. The most commonly affected muscles are those closest to the trunk (hip, thigh, shoulder, neck and upper arm muscles). Apart from being weak, these muscles may be painful and tender as well. In some cases, the joints also become inflamed.
Additional symptoms of dermatomyositis include fatigue, fever and unexplained weight loss. Furthermore, the patients may suffer from lung problems, dysphagia, gastrointestinal ulcers, and calcinosis (which refers to calcium deposits in soft tissues).
Dermatomyositis: What Is the Treatment?
There is no definitive cure for dermatomyositis. However, there are several treatment or management options which can successfully alleviate the symptoms of the condition, improve skin appearance, strengthen the muscles, and stop the progression of the disease. Timely treatment reduces the risk of serious complications.
Medications prescribed to patients suffering from dermatomyositis include corticosteroids to fight inflammation, which are commonly prescribed together with corticosteroid-sparing agents. Corticosteroids are highly efficient in suppression of the immune system. They limit the production of antibodies and consequently reduce skin and muscle inflammation. Corticosteroid-sparing agents are necessary particularly in patients who are using prolonged therapy with corticosteroids. They decrease the side effects of corticosteroids.
If there is no desirable response to corticosteroids, patients may be treated with immunosupressants, antimalarial medications and pain relievers. In some cases patients are administered intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg).
Apart from pharmacological therapy, patients suffering from dermatomyositis may additionally benefit from physical therapy and speech therapy. And surgery is reserved for the most severe cases, namely if there is calcinosis or to solve the problem of recurrent skin infections.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...