Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a very rare inflammatory disease that is characterized by muscle weakness and allergic skin reactions such as for example skin rash. This disease is more common in women than in men and usually happens in adults after they turn 40. If it occurs in children then the years between 5 and 15 are the risk years for this disease.
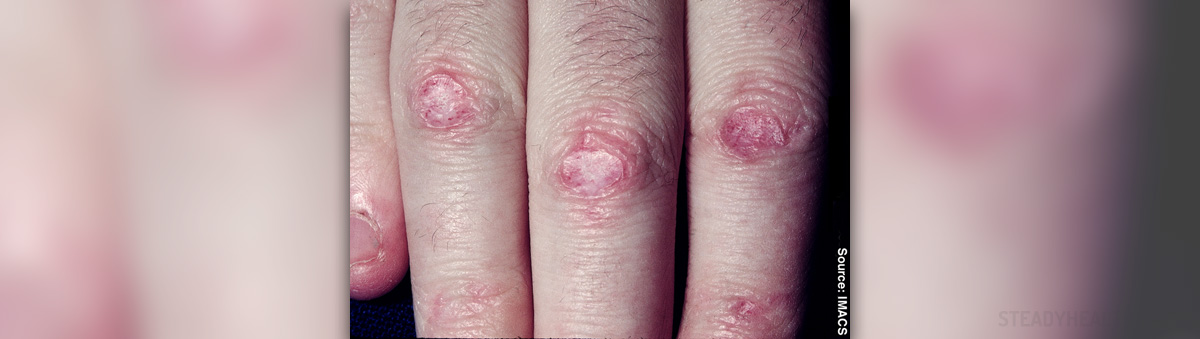
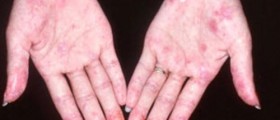
Dermatomyositis has many warning signs and symptoms. The most frequent symptom is the skin rash which is violet or dusky red and which usually appears on the face, back, chest, nails, elbows, and knees. Other symptoms of this disease include muscle weakness, dysphagia, fatigue, fever, as well as weight loss, and problems with the lungs and gastrointestinal tract.
Complications of Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis must be treated on time, because it can cause some serious complications, such as muscle weakness complications, skin symptom complications, and some associated conditions. Muscle weakness complications include problematic swallowing, aspiration pneumonia, problems with breathing, and gastrointestinal problems.
Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing occurs when the muscles in the esophagus are affected by dermatomyositis, thus leading to the loss of weight and malnutrition. In some cases, this condition can even cause the entrance of saliva, food, or liquid into the lungs, which has as a consequence aspiration pneumonia.
Shortness of breath may occur in cases when the muscles of the chest are affected by dermatomyositis. For gastrointestinal problems, gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding are very common. Some complications include infections of the respiratory and digestive tract and calcium deposits in the muscles, skin, and calcinosis or connective tissue.
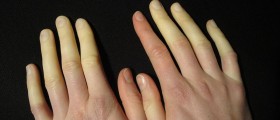
Untreated dermatomyositis can cause some other complications such as Raynaud’s phenomenon, cardiovascular and lung disease, as well as cancer and some connective tissue diseases.
Raynaud’s phenomenon is the medical term for the disease when the fingers, toes, nose, cheeks, and ears become pale in low temperatures. Myocarditis or heart muscle inflammation may also occur as a result of untreated dermatomyositis. Two other cardiovascular problems can also appear such as heart arrhythmias and congestive heart failure.
Interstitial lung disease may also happen along with dermatomyositis. Interstitial lung disease leads to the scarring of the lung tissues. The lungs thus become rigid and the person has a dry cough and problems with breathing.
One of the most serious complications that dermatomyositis can induce is cancer, which usually occurs three years after the diagnosis is set.
Cancer of the cervix, lungs, breasts, ovaries and gastrointestinal tract can develop. Lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjogren’s syndrome are some of the complications that can accompany dermatomyositis.
Treatment
- The standard treatment for dermatomyositis is a corticosteroid drug, given either in pill form or intravenously.
- Immunosuppressant drugs, such as azathioprine and methotrexate, may reduce inflammation in people who do not respond well to prednisone.
- Periodic treatment using intravenous immunoglobulin can also improve recovery.
- Other immunosuppressive agents used to treat the inflammation associated with dermatomyositis include cyclosporine A, cyclophosphamide, and tacrolimus.
- Physical therapy is usually recommended to prevent muscle atrophy and to regain muscle strength and range of motion.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...