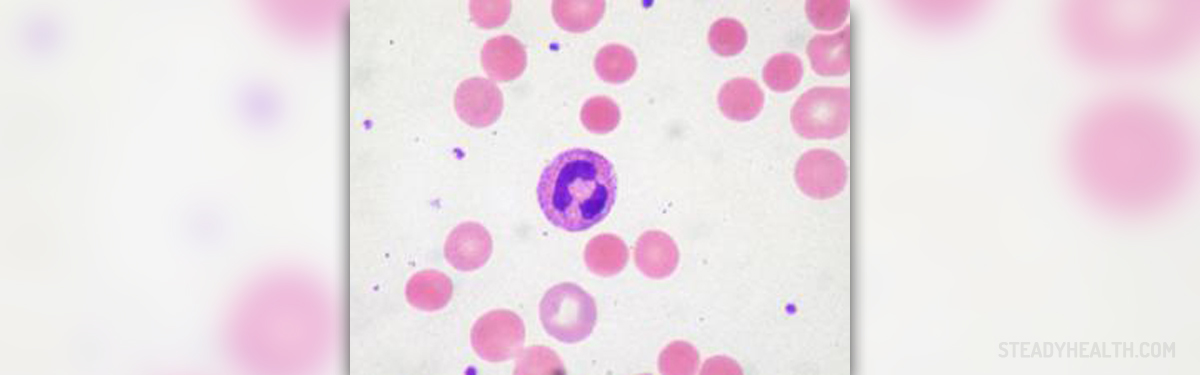
There are the 80 types of autoimmune diseases. They develop when the immune system can’t tell the difference between foreign bodies and healthy body tissue and starts to produce antibodies against healthy organs. Autoimmune disorders are most commonly seen in women, especially African American and Native American women. Most autoimmune diseases have similar symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, dizziness and slightly increased body temperature.
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease that features with inadequate response of the immune system to foods with gluten. When people with celiac disease eat gluten the immune system causes inflammation of the small intestine and damage to the lining of intestinal wall known as villi. This reduces the ability of the small intestine to absorb dietary nutrients which results in nutritional, vitamin and mineral deficiency. Symptoms of celiac disease include anemia, bloody stool, abdominal pain, bone and joint pain, diarrhea, fatigue, oral ulceration, weakness and weight loss.
SclerodermaScleroderma is rare and progressive autoimmune disease of the connective tissue. Scleroderma causes inflammation and thickening of the skin due to formation of scar tissue, or fibrosis. Localized scleroderma tends to be confined to the skin while systematic scleroderma affects internal body organs like heart, lungs, kidneys, bowels and esophagus. Signs of scleroderma include Raynaud’s phenomenon, Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and inflammation of the skin, mostly on fingers, feet, face and neck that leads to skin tightness or hardening. Women are more susceptible to this disease. Exact cause for scleroderma is unknown and the treatment includes corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory medications and Plaquenil.
Polymyositis
Polymyositis is another disease of connective tissue that features inflammation of the muscle fibers. This chronic disease may result in severe weakness because the affected muscles are typically those closest to trunk or torso. Polymyositis most commonly affects people aged between 30 and 50. Apart from weakness, the symptoms include difficulty swallowing and speaking, joint and muscle tenderness, shortness of breath and fatigue. The cause of polymyositis hasn’t been identified and this disease is incurable.
Raynaud’s Disease
Raynaud’s Disease is a rare disorder that affects blood vessels in the fingers and toes. Due to poor circulation of blood to these areas, fingers and toes become numb, cool and change color. This is mostly triggered by cold temperatures. This disease often follows another autoimmune disorder.
Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisThis autoimmune disease affects individuals under 16 years of age. Symptoms of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis include swelling, inflammation, pain, redness and stiffness of joints. The disease cannot be cured and the treatment aims to alleviate the symptoms.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic and progressive disease of the central nervous system. This disease leads to inflammation and destruction of myelin, which provides covering for nerves. Multiple sclerosis results in impaired transmission of nerve impulses, affected muscular control and number of sensory, motor and psychological symptoms.
Wegener’s Granulomatosis
This autoimmune disease represents inflammation of small arteries and veins. This inflammation can damage many tissues and organs in the body such as upper and lower respiratory system, kidneys, eyes, ears, throat and skin. Wegener’s granulomatosis may cause vision problems, hearing problems, cough, skin rash, pleuritis, fatigue, weakness, weight loss and joint pain.
Graves DiseaseThis autoimmune disease most commonly causes overactive thyroid gland. Signs and symptoms include increased heart rate, enlarged thyroid, weight loss, hand tremors, heat sensitivity, sweating, nervousness and sometimes protruding eyes. The treatment includes radioactive iodine.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...