Myositis
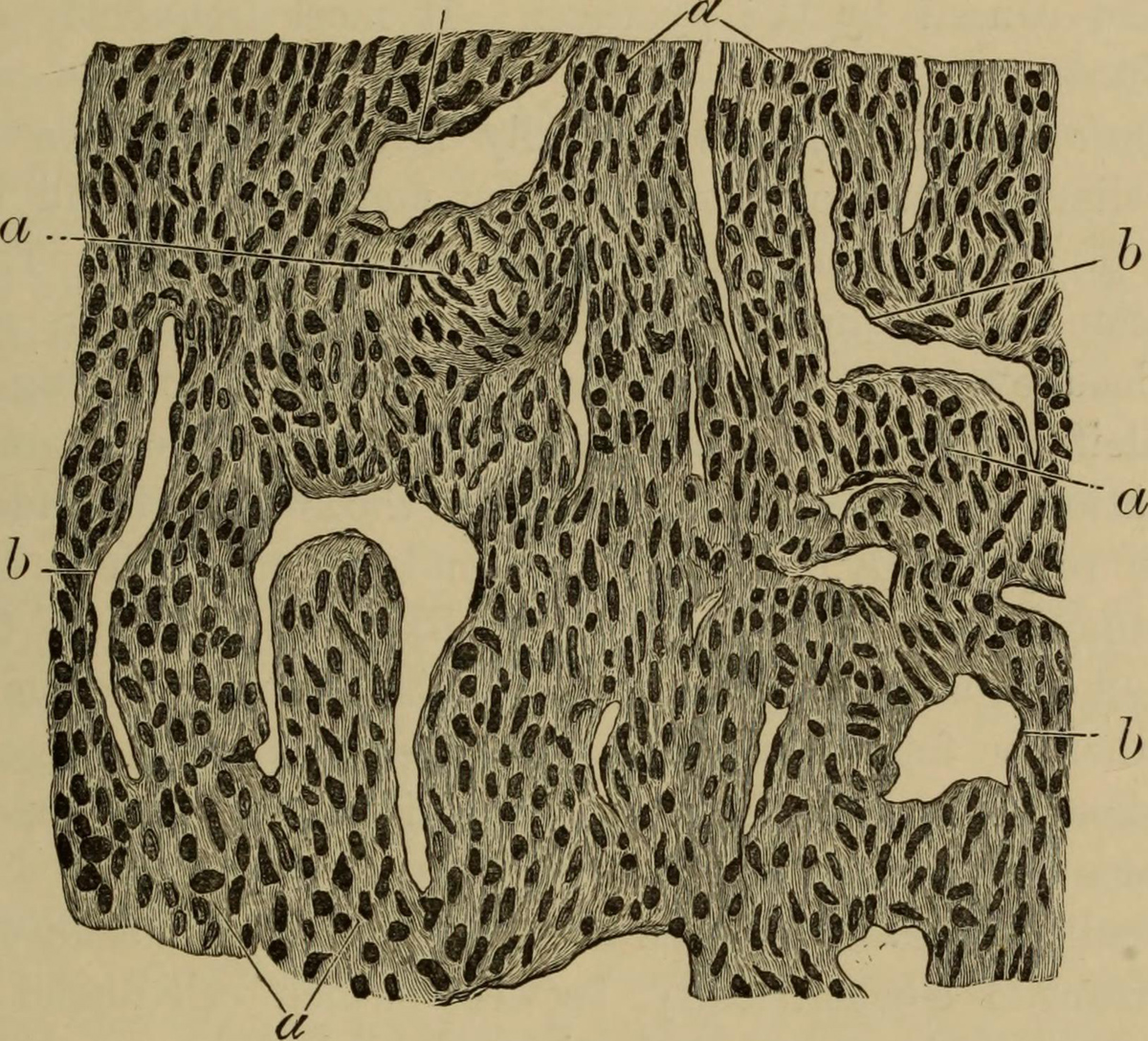
Myosistis is a chronic inflammation of muscular tissue. The term myositis can refer to different kind of muscle inflammation including dermatomyositis, polymyositis and inclusion body myositis. In spite of certain specific characteristics of the previously mentioned illnesses all of them feature with chronic inflammation of the affected muscles. The affected muscles lose their strength and a patient additionally may develop muscle pain. Inflammation is most commonly followed by swelling of the muscles. The inflammation of the muscles does not have to be isolated. In many cases additional organs can be affected by the process of inflammation and these include the heart, joints, intestines, or lungs.
Causes of Myositis
Unfortunately, the exact cause of myositis has not been established yet. Still since there are different types of myositis we can only assume that there are numerous causes involved in the process of muscle inflammation. One hypothesis is based on genetic predisposition. Additionally, people who are predisposed may come in contact with chemicals or some infective agents which are actually triggers of muscle inflammation. It is definitive that the improper reaction of the immune system has something to do with myositis. In autoimmune diseases the body attacks its own cells because it does not recognize them. In some forms of myositis specific antibodies are identified and this is why many doctors actually classify myositis into group of autoimmune diseases.
Antibodies that have been identified in some forms of myositis are also common for other autoimmune diseases. However, there are certain antibodies that are only found and are specific for myositis.
Risk Factors and Incidence of Myositis
This disease is not so common. In the USA it is reported around 5 to 10 new cases in a million. The very diseases can be reported in all age groups. Still it predominantly affects children between 5 and 15 year of age. Additionally, the disease is reported in significant number in people between 30 and 60 years of age. Women are more affected comparing to men. This refers to all forms of myositis except for inclusion body myositis which predominantly affects men more than women.
Diagnosis of Myositis
The diagnosis is set after thorough examination. The doctor will ask a set of questions about the current disease and patient's medical history. Then he/she will examine the patient and perform certain tests. Blood tests will help in evaluation of the presence of autoimmune antibodies and muscle enzymes. Additionally, electromyogram is performed to asses the electrical activity of the affected muscles. A biopsy of the affected muscles is also taken. Apart from the previously mentioned MRI may give excellent insight in current state of the muscles and progression of the disease. And finally, some patients can be easily diagnosed after standard x-ray or CT scan of the affected area has been performed.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...