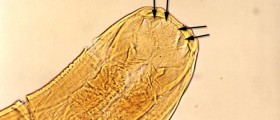
Human parasites may cause many health problems, steal nutrients, secrete toxins, and cause pain in their hosts. It is important to recognize the symptoms of parasites in humans to treat the condition on time and avoid further damage to health.
What are Parasites?
A parasite is an organism that lives in another organism from which it obtains nutrients important for its survival. Since a parasite cannot produce its food, it depends on a host, thus it must find one to survive.
The relationship between humans and parasites is not symbiotic, and only parasites can benefit from a host, while humans may suffer from different infections and illnesses because of parasites. Human parasites live everywhere in our environment and can be ingested through food, water, or air.
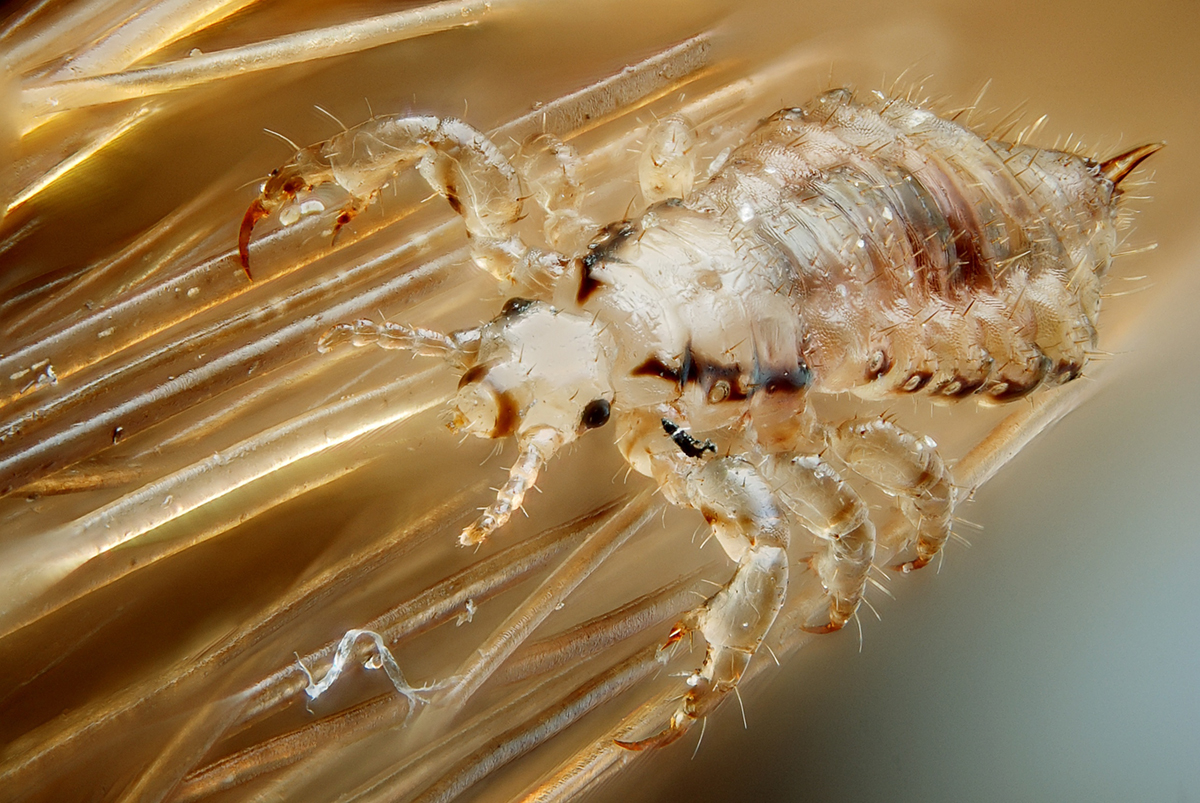

Common Symptoms of Parasites in Humans
Most people do not experience significant symptoms caused by human parasites. However, some common symptoms may indicate human parasite infection. The following symptoms mainly refer to intestinal parasites in humans.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, especially when accompanied by foul-smelling stool, may indicate infection with parasites such as protozoa. Protozoa produce a hormone-like substance known as prostaglandin, which causes sodium and chloride loss in the body and results in frequent watery stool. There may be even traces of blood present in the stool.
Constipation
Another common symptom of intestinal parasites is constipation which can be caused by the large size and shape of certain worms. These worms can obstruct the bile duct and the intestinal tract leading to irregular bowel movements.
Anemia
Anemia may occur due to the presence of a large number of certain worms, such as human tapeworms. They can leach vital nutrients from the human body and draw out the blood, causing iron deficiency and anemia.
Bloating and Gas
Intestinal parasites may cause inflammation of the intestines leading to bloating and flatulence. If this condition persists and isn’t associated with foods, it indicates the presence of intestinal parasites.
Muscle and Joint Pain
Certain parasites live in joint fluids and muscles and cause inflammation as a result of tissue damage. This causes a lot of pain in muscles and joints.
Fatigue
Fatigue may occur due to human parasites because they take away vital nutrients and lead to the malabsorption of vitamins, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. This may also cause symptoms, such as depression, tiredness, apathy, and impaired concentration.
Allergies
Allergies may occur because the body may respond to intestinal parasites by producing antibodies, such as eosinophils. The eosinophils can cause inflammation of the body tissues and lead to an allergic reaction. This includes food allergies, hives, rashes, ulcers, swelling, and sores.
- A total of 1,301 participants aged 22 days-90 years were enrolled in this study. We used a structured questionnaire to obtain socio-demographic and stool examination to investigate intestinal parasite infections. Data analysis was performed using SPSS16.
- The overall prevalence of intestinal parasites (IPs) was 32.2% (419/1,301). Three hundred and fifty nine cases/1,301 (27.6%) were infected with a single parasite and 60/1,301 cases (4.6%) presented polyparasitism.
- The most common IP was Blastocystis sp. 350/1,301 (26.9%), followed by Entamoeba coli 38/1,301 (2.92%), Giardia lamblia 30/1,301 (2.3%) and Cryptosporidium spp. 17/1,301 (1.3%). Regarding the socio-demographic variables, educational status (p = 0.001), contact with domestic animals and soil (p = 0.02), age above 15 years (p = 0.001) and seasons (p = 0.001) were significantly associated to intestinal parasitic infections.
- Concerning clinical characteristics, the presence of IPs was significantly associated to diarrhea (OR = 1.57; CI 95% = 1.24-1.98; p
- Worldwide, previous studies have shown that there are several risk factors associated to the high prevalence and incidence of IPIs including untreated water supply, age, poor sanitation, low family income, low level of education, low level of parental education, eating unpeeled/unwashed vegetables and fruits, contact with livestock or pets and poor personal hygiene.
Other Symptoms of Human Parasites
Other symptoms that a person affected by human parasites may experience include: nervousness, irritable bowel syndrome, insomnia, heartburn, nausea and vomiting, loss of weight and constant hunger, itching around the nose, ears, and anus, and chronic ear and sinus infection.












_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...