Definition of a Parasitic Disease
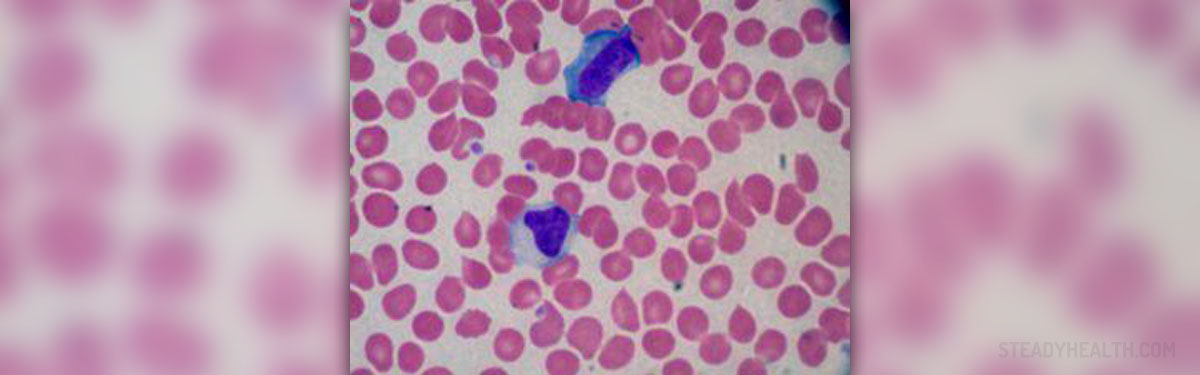
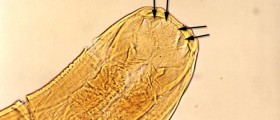
A parasitic disease is an illness caused by the presence of a parasite, which receives nutrients from the host organism. The study of parasites is called Parasitology, and it postulates that not all parasites lead to diseases, while those that do can affect different organisms, from plants to humans. There are different ways in which the presence of parasites can bring about various diseases. Some will produce adverse effects directly, simply by coming into contact with another organism. Others will leave poisonous substances which consequently lead to the development of illnesses. In addition, there are three distinct types of parasites. The protozoa and helminths are the types of parasites that exist inside the organism, while ectoparasites abide on its exterior. It should be noted that there are many bacteria that operate as parasites. When it comes to the symptoms of diseases that are caused by parasites, they often appear as those of various types of hormonal imbalances or the body’s lack of red blood cells. Parasites such as worms produce problems which include constipation, loose bowel, vomiting, abdominal pain, pain in joints and muscles, and an overall feeling of weakness. In many cases such symptoms can be confused with food poisoning. Diagnosing a parasitic illness can be challenging as the symptoms resemble those of many other disorders, but there are various simple tests that a medical care provider will administer, such as a blood test and a stool sample test.
Parasites Transmit Infectious Diseases
There are numerous ways in which humans can get infected by parasites. For instance, one of the most common ways is through consumption of contaminated food or drink or by eating raw or rare types of food. Engaging in unprotected sexual conduct or coming into close physical contact with someone who is infected are another pathways to parasitic diseases. As parasites usually enter the body through mouth or skin, insect bites are often known to lead to problems caused by parasites. Further, cats and dogs carry many kinds of parasites so individuals who are prone to infections or have weak immune systems can easily become ill after coming into contact with those animals. Having inadequate personal hygiene is another certain course to parasite diseases. When it comes to the problems which are brought into effect by parasitic illnesses they range from relatively mild discomfort to severe problems which might culminate in death. Many parasitic infections attack the red bloods cells as well as lead to protein deficiency. Such contamination poses a particular threat to people in the developing world, where close to 750 million individuals are affected by some form of a parasitic disease. Worm infections represent a critical problem for children who are chronically affected, as well as for pregnant women. Parasitic diseases are widespread in tropical areas, with Malaria being the primary parasitic illness resulting in over 1 million deaths every year. There are also numerous forms of neglected tropical parasitic illnesses that affect about 1 billion individuals, and can have adverse consequences on children’s development, as well as the prosperity of whole communities and countries. Other than in tropical climates, parasitic diseases are present in the developed world where they also affect millions of individuals, and lead to severe illnesses and death. When it comes to treatment, there are medications that are regularly administered. However, parasites easily become resistant to many forms of drugs and as a result recreate infections making it a very expensive problem to deal with. There are parasitic diseases for which there are no medications. In such cases only the symptoms are treated until the infected individual returns to normal.
List of the Most Common Parasites
As previously mentioned, there are numerous types of parasites which cause illnesses in humans. Helminths, for instance, are worms that reside in humans and are visible without a microscope. They cannot, however, multiply once they enter the human body but they can cause problems in both their larval and fully grown stages. Another kind of parasite that attacks humans is the Protozoa. Protozoa are a type of parasite that only consist of one cell, but are able to multiply and survive easily. Those protozoa that exist in the intestines are transferred from person to person either through close physical contact or via contaminated food or drink. The protozoa that reside in tissue or blood are conducted through insect bites. Similarly to helminths, there are numerous kinds of protozoa as well. Also, there are parasites grouped under a term ectoparasites, which are in most cases fully grown organisms visible to the naked by, but depend on others for their food supply. Ectoparasites include lice, fleas, and ticks and they do not produce any toxic substances that leave adverse effects on humans. Rather, they are the carriers of distinct elements that produce diseases.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...