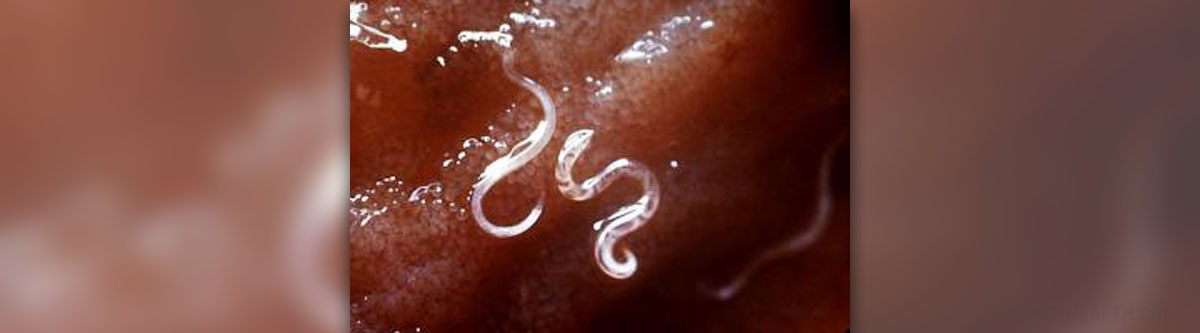
Parasites are living organisms that require a different organism or a host in order to grow, feed and survive. From this relationship, only parasites gain benefit as they take away all the nutrients from the host. Humans can be hosts for more than a thousand types of parasites. Parasites can enter the human body through contaminated air, water or food. Parasites usually infect human digestive tract. Once they enter the intestines, they do not only absorb nutrients but suck blood and tissue and may cause intestinal obstruction. Intestinal parasites in humans can cause weakness, malnourishment, low immunity and increased susceptibility to infections and different diseases.
Types of Intestinal Parasites in HumansProtozoa
Protozoa is a one-cell microscopic organism that can reproduce in the human body. Protozoa usually infect humans through contaminated water or food. Also, protozoa can be transmitted through the fecal route. There are numerous species of protozoa but the most common are amoebae, giardia, neospora, toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidium and sarcocystis.
HelminthsHelminths are wormlike parasites with size that can range from a few millimeters to several meters. Common helminthes that infect humans are tapeworms, pinworms, hookworms, threadworms, roundworms and flukes. Adult intestinal worm can not reproduce inside the intestines but can seriously impair human health.
Symptoms of Intestinal Parasites in HumansParasites can live in the human intestines for years without causing symptoms. However, common early symptoms of intestinal parasites in humans can be diarrhea, bloating, nausea and constant anal itching. Sometimes, an infected person can also experience runny nose, restlessness and blisters on the mouth. Increased appetite, headaches, joint pain, chronic fatigue, allergy-like symptoms and autoimmune deficiencies can be present too. Untreated intestinal parasites can cause bad smelling stools or mucous and blood in the bowel movement. There may be flu-like symptoms, abdominal cramps, loss of appetite, pale skin, gas, rash and itching. In rare cases, an infected person may pass worms in the stool.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Intestinal Parasites in HumansIn order to see if a patient is infected with parasites, a health care provider will order urine, stool, blood, sputum and skin tests. These tests can also show which type of parasite is present. Apart from these tests, scotch tape test and string test can also be used. If diagnostic tests confirm presence of intestinal parasites, there are several treatment options available. Most commonly prescribed anti-parasitic drugs are mebendazole, thiabendazole, metronidazole, praziquantel and diphenoxylate. Cleansing of the intestinal tract can also help to eliminate intestinal parasites. There are natural remedies that can be used in treatment of intestinal parasites such as garlic, pomegranate, vasaka, wormwood, clalamus, black walnut, curl mint, barberry, pumpkin seeds and others.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...