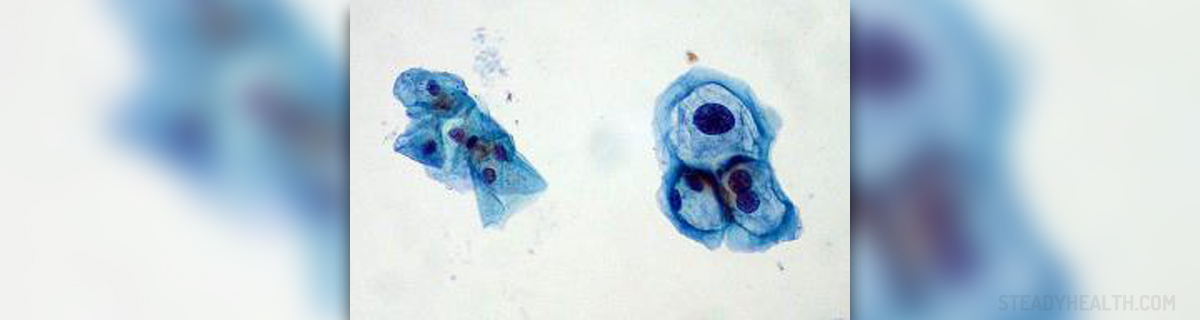
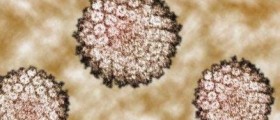
Genital human papillomavirus, also known as HPV, is one of the most commonly sexually transmitted infections. There are about 200 different kinds of viruses from this family and they may cause an infection to the male and female genital areas. Sometimes these viruses are able to infect the mouth and throat. A great majority of these viruses do not cause any symptoms in humans, some others are responsible for genital warts (verrucae), while a minority of viruses may cause cancers of the cervix, vulva, vagina and anus in women and cancers of the anus and penis in men.
Infection
The HPV virus is passed through the sexual intercourse and genital contact. Most commonly it is passed during vaginal and anal sex. It may also be passed through oral sex. The problem with this virus is that people may be unaware of its presence for years and continue passing the virus on to other sexual partners.
In rare cases, an infected mother may pass the virus to her child. If this happens, the child may develop Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP).
The average incubation period is approximately two to three months, but it isn’t unusual if the full symptoms develop earlier or even later – up to 20 months after the first exposure to the virus. The virus infects the top layer of the skin and it may be latent for years before the first signs of the HPV infection appear.
It is not certain for how long the infected person stays contagious. Many scientific researchers are focused on this question. There is a possibility that HPV virus stays in the body of a carrier forever but it isn’t yet clear if the person stays contagious till the rest of the life or the virus becomes latent after some time.
Symptoms of HPV infection
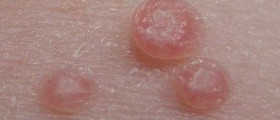
HPV infection may appear as a genital wards disease characterized by small bump or groups of bumps in the genital area. Sometimes they look like a tiny cauliflower, because of their rugged surface. They are differently shaped, may be small or large, raised or flat. If left untreated they will eventually go away or increase in the size and number. However, these wards are not going to turn to cancers.
Cervical cancers do not show any symptoms in the early stages. However, regular medical examinations and screening tests may detect the early signs of the infection and treat the problem before it turns to cancer. Other kind of cancers related to HPV virus may also be hard to spot in the early stages. However, any change in the genital area should be considered as a warning sign.Prevention
There is no 100% working method to prevent the spread of HPV virus. Even condoms, which are considered to be the safest means of protection against the sexually transmitted diseases, may not give the complete protection. This virus may spread from all of the genital areas, which are not covered with condom. The only reasonable prevention method is to limit the number of sexual partners and choose partners carefully. The only absolutely confident way to prevent HPV is to avoid all sexual activity.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...